Data quality and completeness for products and entities, in the form of sufficiency scores, can be obtained by configuring metrics, business rules, and specific parameters within a Sufficiency Configuration Type. These sufficiency scores, at a minimum, can:
- define data profiles that determine the quality of data
- control an item's movement through a workflow by determining certain requirements for passage
- search for items based on certain sufficiency metrics
- measure data sufficiency against a predefined syndication channel on an external system
Note: The terms 'Sufficiency Configuration Type' and 'Sufficiency' are used interchangeably throughout the documentation that addresses sufficiency scores and data quality and completeness, and both terms refer to the same functionality.
To achieve an overall better understanding of how sufficiency scores are obtained, it would be beneficial to look at an example as to how the order of actions occur to obtain a sufficiency score from a Sufficiency Configuration Type:
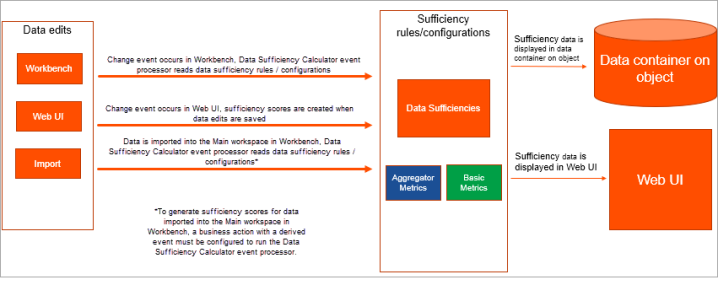
-
A change event occurs as a result of edited data. An example of this is when an attribute value on a product or entity is changed.
-
If a change event occurs in the workbench or data is imported, the Data Sufficiency Calculator event processor runs, reads the data, and calculates scores / messages based on the settings (i.e., metrics, business conditions, etc.) that are configured within the Sufficiency Configuration Type. If a change event occurs in the Web UI, the sufficiency scores /messages are created when data edits are saved.
-
The sufficiency data is stored within a data container in the workbench and can be viewed in the Sufficiency Panel in the Web UI.
Note: While sufficiency scores can be viewed within data containers in the workbench, data sufficiency messages within the workbench are not human-readable and should only be considered as an indicator that messages have been processed. These values are human-readable within the Web UI, where they can be viewed in the Sufficiency Panel.
Prerequisites
Important: For the sufficiency scores to be correctly evaluated for both products and entities on the same system, each Sufficiency Configuration must have a business condition added to define whether the Sufficiency Configuration should be evaluated for product or entity object type(s). The same sufficiency cannot run on both a product and an entity as any given data container type can only be valid on one supertype. However, sufficiencies can run only on products and others can run only on entities. All sufficiencies require a condition to specify the object type that they should act on, without the condition, errors are returned. Also, sufficiencies do not work for classifications because a data container cannot be made valid for a classification object type.
Several features work together to deliver sufficiency scores and separate topics are available to make the process as clear and concise as possible. To navigate creating sufficiency scores based on data quality (and more precisely, obtaining sufficiency scores via a Sufficiency Configuration Type), users should follow the steps listed below in order:
-
Create the metrics that will be used within the sufficiency.
Metrics are an essential element of sufficiency scores and having a firm grasp in understanding how metrics work, both separately and combined with other metrics, is crucial to the success of obtaining accurate and usable sufficiency scores. For more information, refer to the Metrics topic.
-
Create and configure the Sufficiency Configuration Type.
The Sufficiency Configuration Type stores metrics, business actions, business conditions, selected contexts, etc., to create sufficiency scores for object data (refer to the 'Important' message at the beginning of the Prerequisites section). For more information, refer to the Sufficiency Configuration Type topic.
-
Configure the Data Sufficiency Calculator processing plugin.
The Data Sufficiency Calculator processing plugin works with the Sufficiency Configuration Type to calculate sufficiency scores for a given product or entity and returns those scores to data containers in the workbench and to the Sufficiency Panel within the Web UI. For more information, refer to the Data Sufficiency Calculator Processing Plugin Parameters and Triggers topic.
Note: Depending on how data is generated / edited, the Data Sufficiency Calculator processing plugin may not be necessary when creating sufficiency scores. Refer to the diagram at the beginning of this topic for details.
-
Understand the Sufficiency Panel for Web UI.
Although it is not part of the initial setup, it is recommended that users are familiar with the Sufficiency Panel which displays sufficiency scores for a given product or entity in the Web UI. Sufficiency scores represent data quality using numbers, colors, and messages. For more information, refer to the Sufficiency Panel topic.
Resources
Refer to the Setting Up Privileges Example topic in System Setup documentation for information on setting privileges.
This table includes information on privileges required to create and maintain sufficiencies.
| Functionality | Privileges | For more information |
|---|---|---|
|
Sufficiency Indicators |
Maintain Data Container Type [Additionally, other necessary privileges to edit attributes.] |
Refer to the Below Title Sufficiency Card topic and the Product Editor Screen topic in the Web User Interfaces documentation. |
|
Sufficiency Panel |
Maintain Data Container Type View Setup Group View Setup Entity |
Refer to the Sufficiency Panel topic. |
|
Calculating and Viewing Sufficiency Scores |
Create data container Modify metadata for product (property value) (also translate) Modify metadata for entity (property value) (also translate) |
Refer to the Sufficiency Configuration Type topic. |
|
Data Sufficiency Calculator Processing Plugin Parameters and Triggers |
[Users creating event processors needed for this calculator will need adequate privileges.] |
Refer to the Action Sets section and the Users and Groups section in the System Setup documentation. |