This topic provides a beginner-level overview of STEP's translation capabilities and assumes that the user has a working knowledge of the STEP system. In this topic we will discuss the kinds of objects that are suitable for translation, the various ways STEP enables users to translate content, and a primer on the various terms and statuses users are likely to find while exporting content for translation. Detailed guidance covering other aspects of the translation process, like executing XML and Excel exports, importing files, and handling errors, can be found in their own topics.
STEP enables translation of a wide range of data. Using language-driven contexts, multiple translations can be created for a single STEP object. This allows an object to be translated into multiple languages while the core object retains all translated data and inter-language connections.
Briefly, STEP translation works like this: when a user exports, for example, a product hierarchy for translation, all language-dependent attribute values for those products are extracted for translation. The content is then translated, often by a translation vendor, and imported into STEP. All translated values flow into the appropriate attribute in the relevant language context. The second time that same product hierarchy is extracted for translation, the attribute values are evaluated as part of an automated process, and only those values that are new or have amended content are extracted for translation.
It is important to note that STEP enables data to be translated but does not translate data itself. Throughout the guidance on this subject you may view references made to 'starting translation' in STEP. This statement refers to the act of exporting the to-be-translated content from STEP so it may be sent elsewhere for translation.
Translatable Objects
The object types in STEP that may be translated are:
- Products
- Classifications
- Asset names (names of images and documents, for example)
- Product values
- Index words
- LOV (List Of Values)
- Units
- Attribute names
- Free text cells in tables
Translation Methods
The following methods are available in STEP to extract data for translation:
- Structured translation: Translatable data is exported from STEP into either an XML or Excel file. The file can then be imported into the translation vendor's translation memory tool. Once the data has been translated and sent back from the translation vendor, the updated file can be imported back into STEP, bringing all translated data into its relevant context. It is useful to note that translation XML files can only be produced using the structured translation method.
- Manual Excel translation export: A more targeted export of translatable data into an Excel file. This method is often used to quickly send small amounts of data to a translation vendor to address a late change to already-exported data. Once the data has been translated and sent back from the translation vendor, the Excel file can be imported back into STEP, bringing the translated data into its relevant context. All objects can be translated using this method, except free text cells in tables and reference / link metadata.
- Manual translation: Data is translated directly in STEP, either by allowing a third-party translation vendor direct access to STEP or by allowing an internal resource fluent in the target language to translate directly in STEP.
- Asynchronous translation: For customers who engage translation vendors SDL or Lionbridge or use the Across Language Server translation software to translate their content, a REST API can be set up that will enable automatic transmission of translated content (in XML format) between STEP and the translation servers. Another asynchronous option, the File Exchange Service, allows users a way to export and/or import translation files to folders instead of using a translation service API.
Not all object types can be exported for translation into an XML and Excel file. The table below shows which translation methods are available for which objects.
| Translatable Object | Structured Translation | Manual Excel Translation | Manual Translation | Asynchronous Translation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XML Translation | Excel Translation | ||||
|
Product, classification, asset names, and values |
|
|
|
|

|
|
Index words |
|
|

|

|

|
|
Free text cells in tables |
|
|

|

|

|
|
LOVs |
|
|
|

|

|
|
Units |
|
|
|

|

|
|
Attribute names |

|
|
|

|

|
|
Reference / link metadata |
|
|

|

|

|
*Exception: not available for LOVs configured a) to disallow new values or b) without value IDs assigned to the LOV's values.
Translation Relations
In most instances, the objects being translated are subject to revision control, which requires that the data be approved before it can be exported for translation. This requirement is in place to ensure that different revisions of an object in translation remain clearly defined. Once the translation is complete, a translation relation is established from the source language to the target language.
Note: Users have the option to turn the approval requirement off in the 'Object Selection' screen in the Request Translation wizard. By leaving the 'Completely Approved Source' option unchecked on the 'Approval Requirement' parameter, an object need not be completely approved to be exported for translation, though only content from the Approved workspace will be included in a translation export. If, however, an object has never been approved, that object will not be exported even if the 'Completely Approved Source' box is unchecked.
A translation relation refers to the relationship between an object's source language and the language the object is being translated into, also known as the target language. For instance, if you translate an object in US English into French, German, and Italian, you have created three translation relations: US English to French, US English to German, and US English to Italian.
Translation of Local and Inherited Values
All values that are unique to a given object – also known as 'local' values – are extracted for translation. Local values are non-inherited values; they are added directly to a given object.
Inherited values are values that are inherited from other objects at a higher level. They can be identified by a green inverted triangle symbol (![]() ) that appears in the icon column. If an inherited value has already been translated at a higher level, it will not be extracted for translation. When an inherited value is overwritten or revised in any way on a given object, it becomes a local value to that object. If that higher-level value is then edited, that edit will not affect the now-local value as it is no longer inherited from that higher-level value.
) that appears in the icon column. If an inherited value has already been translated at a higher level, it will not be extracted for translation. When an inherited value is overwritten or revised in any way on a given object, it becomes a local value to that object. If that higher-level value is then edited, that edit will not affect the now-local value as it is no longer inherited from that higher-level value.
For more information on inheritance, refer to the Inheritance in the Product Hierarchy topic in the Getting Started documentation.
Translation terms
When managing translations, it is important to understand the terms that reference the various languages involved in the translation process:
- Master language: The first language used as source language
- Source language: The language from which a translation originates
- Target language: The language being translated into
A source language may be translated into as many target languages as have been set up on a given STEP system. In the screenshot below, you can view the Status tab on an object. The user has selected English as the master language for this object. The user has also elected to translate the object into five target languages: UK English, German, Hebrew, French, and Danish.
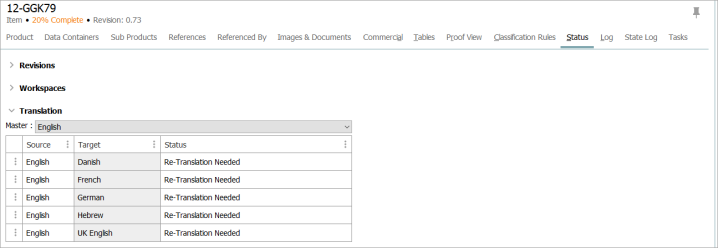
Translation Status
On each classification, product, attribute, or asset, you can view an object's translation status, which is the value appearing in the Status column in the above screenshot. There are two ways to view the translation status of an object:
- In the Tree, select the relevant object, and then click the Status tab. The view will resemble the screenshot above.
- In the Search tab, search for the translation status of specific object types. For more on searching for translation status, refer to the Searching for Translation Status topic.
In the collapsible Translation section of the Status tab content, the third column is 'Status.' For each Translation Relation listed in this section, a status is displayed. One of the three statuses listed below will appear:
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
|
Re-Translation Needed |
Translated content in the source language has changed since the most recent translation completed. This status indicates a re-translation from the source into the target language is needed to bring all content up to date. |
|
Up to Date |
No translated content in the source language has been changed since the previous translation. Translation from source language into target language is up to date. |
|
In Progress |
A translation extraction has been done and is currently running as an active background process. Once the translated content has come back from the translation vendor and the file has been imported, the background process will complete and the status will update to Up to Date. |
Additional settings can be applied to all STEP translations by accessing the 'Users & Groups' node on the 'System Setup' tab in the workbench. This is where users can configure how translation files are named, whether the 'Filter spreadsheet' parameter should display in the 'Request Translation' wizard, and, if so, what the default value should be, and what attributes should always be excluded in translations. For more information on these settings, refer to the Translation Settings topic of the System Setup documentation.