This topic will cover the process of importing a translation XML file into STEP.
Once the translation vendor has completed translation of the submitted objects in an XML file, the XML file can be imported into STEP. Importing a translation XML file into STEP will bring all of the new translated values into the appropriate language contexts.
After the user has initiated an import, but before the import is executed by the system, STEP takes a series of automated steps to ensure the translated content is handled correctly. Prior to executing an import STEP will:
- Check that the XML is valid (not malformed)
- Check that no values in either the source or target language have been modified in STEP since the XML file was exported
- Check that the imported values match the attribute validation base types in STEP (for instance, if an attribute restricted to accept only number values is given a free text value, an error is raised)
To start the translation Import Wizard, click File > Translate > Import Translation...
Step 1 - Select file
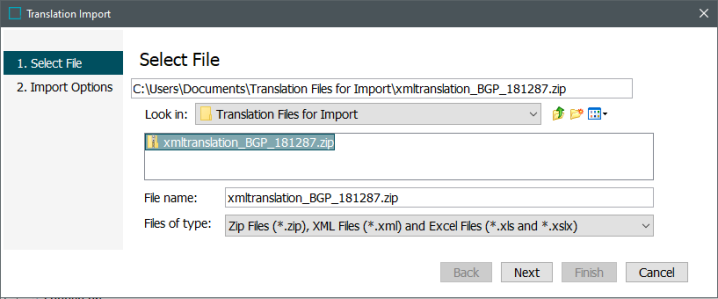
In the Select File step of the Translation Import Wizard, the user must select the XML file to import. To select the relevant file, navigate in Windows Explorer to the location of your file and select it. Then click Next.
Note: Users may name the import file according to whatever naming convention is most useful to them. The import process keys entirely off the contents of the file, not the file name, so users have complete freedom in naming import files. The file must either be an .XML file or a .ZIP file with an .XML contained inside.
Step 2 - Import Options
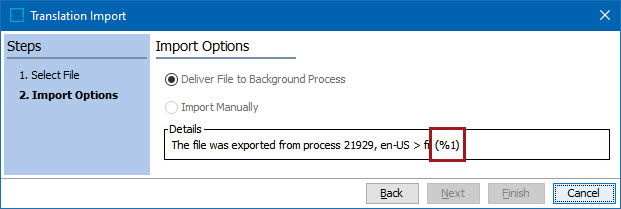
The first option available on this screen, Deliver File to Background Process, is selected because you have elected to import an XML file. Deliver File to Background Process is the best option.
If the user selects the Import Manually option, a message in red text will appear in the Details section:
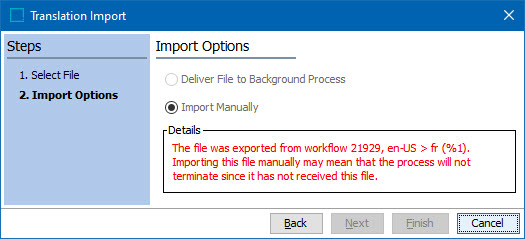
The last sentence states that, "Importing this file manually may mean that the process will not terminate since it has not received this file." What this means is that because the user intends to import the file manually, the file will not be delivered to the background process created to export the XML. The background process is paused at 50 percent post-export, and will not advance to completion (100 percent) unless the file is delivered back to the background process. This means that if the user selected Import Manually, the translated data may be correctly updated, but the background process will never advance. If the manual import completes with no errors, users may update the values in the XML file and import it using the structured import. The background process will complete.
The primary advantage of Import Manually as it relates to XML files is that it allows a user to import verified data directly into STEP without the added steps of addressing a background process or forcing the data through STEP's validation process. In practical terms, if a third-party translator has multiple changes to the same translation, manually importing each updated XML file can be the most efficient way to update the translation quickly.
With Deliver File to Background Process selected, click Finish. A File Uploaded to Process window displays with a message like the one below:
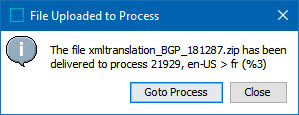
To check the progress of the import, click Goto Process. This will take the user to the background process executing the import.
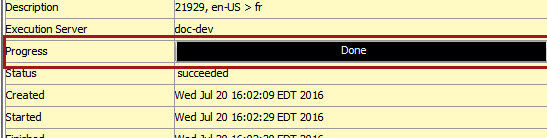
Once the user has accessed the background process, they should view that:
- the Progress bar, which was halfway across and paused at 50 percent, is complete and shows a Done status.
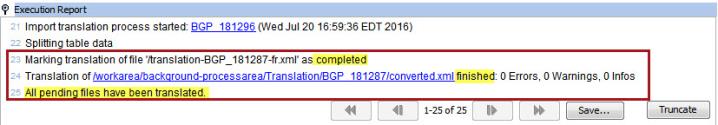
- the final steps listed in the Execution Report section of the background report show that STEP has marked the "translation of file" complete, and further states that "all pending files have been translated".
To ensure the translated values were updated as planned, the user may select one of the translated objects, switch the Context to the target language's context, and find one of the values that was set to translate. The translated value should display.
For information on how to import Excel files, refer to the Importing Translation Excel Files topic.
For more information on how to handle errors that may arise during import of a translation file, refer to the Handling Translation Errors topic.