This topic will cover the process of importing translation Excel files, both via the structured translation process and through the Manual Excel Translation Export, back into STEP. A successful import will complete a translation task.
When the translation vendor has completed translation of the submitted objects in an Excel document, the Excel file can be imported into STEP. Importing an Excel file will bring all of the new translated values into STEP in the appropriate language contexts.
After the user has initiated an import, but before the import is executed by the system, STEP takes a series of automated steps to ensure the translated content is handled correctly. Prior to executing an import STEP will:
- Check that the Excel file is intact, meaning no sections have been deleted or amended
- Check that no values in either the source or target language have been modified in STEP since the file was exported
- Check that the imported values match the attribute validation base types in STEP (for instance, if an attribute restricted to accept only numerical values is given a free text value, an error is raised)
To start the Import Wizard, click File > Translate > Import Translation...
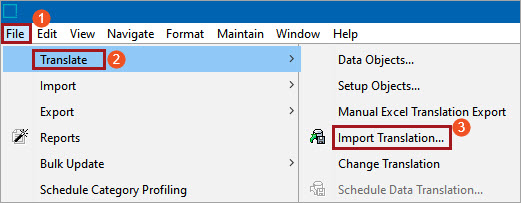
Step 1 - Select file
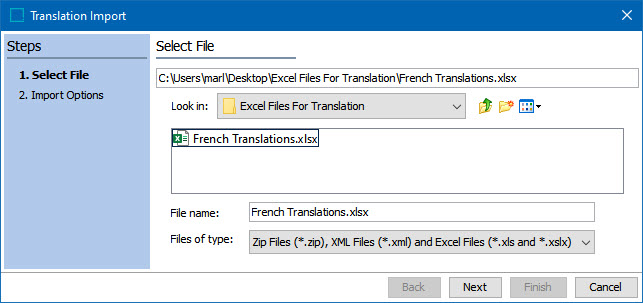
In the Select File step of the Translation Import Wizard, the user must select the Excel file to import. Navigate in Windows Explorer to the location of your file and select it. Then click Next.
Note: Users may name the import file according to whatever naming convention is most useful to them. The import process keys entirely off the contents of the file, not the file name, so users have complete freedom in naming import files. The file type must be an .xls or .xslx file.
Step 2 - Import Options
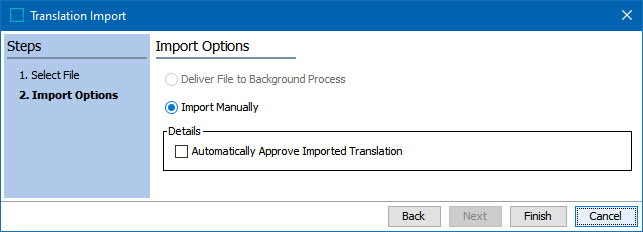
The Import Options step of the Translation Import process will provide different options depending on whether the Excel file to be imported was done as part of the structured translation process or as a Manual Excel Translation Export.
If the import file was initially generated through the structured translation process, both import options, Deliver File to Background Process and Import Manually, will be available. Make your selection and click Finish.
If you select Deliver File to Background Process, a message screen will display showing the process number assigned to the import action, as well as an option to go directly to the background process executing the import.
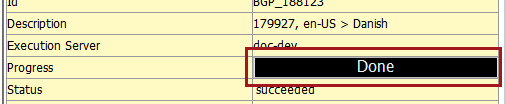
If the user elects to go to the background process, and there are no errors, they will view that:
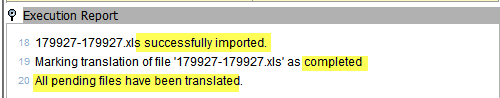
- the Progress bar, which was halfway across and "stuck" at 50%, will complete and show a Done status.
- the final steps listed in the Execution Report will show that STEP has marked the "translation of file" complete, and states that "all pending files have been translated".
The user may also select Import Manually for an Excel file generated through the structured translation. If the import file was initially generated through the Manual Excel Translation Export process, then Import Manually will be the only available option. After selecting Import Manually, click Finish and the updated values will be added to the pertinent language. No background process is generated by this action. Any errors that occur will be surfaced in a dialog that will enable a user to Save, View, or Discard an error report.
Users importing Excel files will have the option to Automatically Approve Imported Translation.
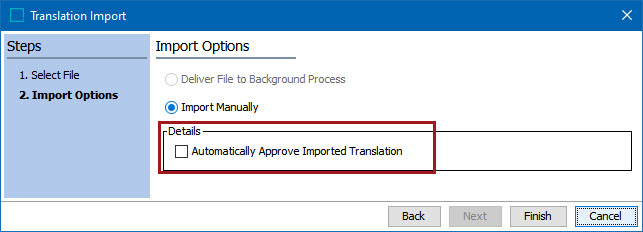
Checking this box automatically changes the status of the object in the target language to Approved once the import completes. The benefit to checking this box is that it removes the added step of manually approving the object in the target language after an import. When multiple translations are executed, removing this step can represent a significant time savings.
To ensure the translated values were updated as planned, the user may switch the Context to the target language's context and find the values that were in the green-shaded cells. The translated values should appear in the object record.
In some instances, these processes may generate errors. For more information on the kinds of errors you may encounter, refer to the Handling Translation Errors topic.