A 'tag' is a markup notation used to indicate specific formatting or special characters. A tag is identified by a unique tag name, and is available to be inserted into text based attributes in both the workbench and Web UI.
Tags are maintained in System Setup in the Tags folder.
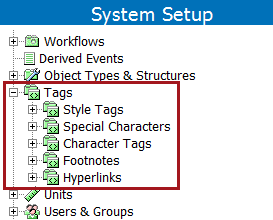
All tags in STEP are 'media neutral.' This means that data entered into and maintained in the STEP system is independent of whatever media it delivers exported files to. There are no embedded codes within the data that are specific to any one type of media, such as HTML. This means that STEP solves the issue of users having to enter media-specific command codes within the data stream. In this way, the same attribute could be output to any media and provide the necessary command codes that are relevant to that output media.
STEP supports several different types of output, including but not limited to InDesign, Microsoft Word, web applications, and any number of custom applications.
Tag Systems in STEP
There are two systems of tags in STEP:
- 'Paired tags' (such as style tags, hyperlinks, and footnotes) have a separate start and stop tag, e.g., <bold>xxxx</bold>.
- 'Unpaired tags' (such as special character and character tags) do not have a separate start and stop tag. Instead they are 'self-contained', e.g., <in/> or <ft/>.
For every STEP tag created the user can define what the appropriate corresponding command codes are for different media outputs. For example, the <bold> </bold> tags may be converted to <b> and </b> for an HTML3 output format, <ct:Bold> and <ct:> for the InDesign output format, or the tags could be stripped out entirely for a custom output format.
Types of STEP Tags
These are the main tag types:
Special Character
Special Characters are Unicode characters, which in some cases need to be formatted. Examples are the Greek characters α β γ. These characters are valid Unicode characters and can be entered into any text element or into product data. To make these characters output to a printer or to output properly in, for example, InDesign, a formatting has to be set up.
Character Tags
Character tags allow users to maintain STEP tags within the system and convert them to one or more characters used in special fonts upon exporting the data. Sometimes these characters are known as Dingbats. For example, they can be used to export non-Unicode characters (or any other character or characters that are not Unicode characters) such as a telephone  or a special arrow
or a special arrow 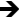 .
.
Style Tags
Style tags apply changes to how text looks. For example, it can make plain black text bold, blue, or can format text as a list with bullets or numbers. Style tags must have an opening and closing tag, for example, <bolditalic> </bolditalic>. Style tags are used with STEP Tables in order to apply styling to the contents of table cells.
Footnotes
Footnotes are used in STEP Tables only to add an additional piece of information to attribute values when the attributes are used. If footnotes are added to attribute values outside of a STEP Table, they will not output expected result. Footnotes are added / edited within the Rich Text Editor, so using these options will open that dialog. They are also required in order to use the Footnote Transformation within STEP tables. For more information, refer to the Tables documentation here.
Hyperlinks
Hyperlinks are used to define the formatting of hyperlinks when they are used in attributes with the value base type as 'text'. The hyperlink can either precede, come in the middle of, or come after the designated text.
Note: Hyperlink tags are not attributes with the validation base type of a 'URL'. Attributes with the validation base type of a URL do not allow for any text other than a URL in the value field.
Working With Tags
Follow these topics to use tags in STEP:
- Create tags - refer to the Creating Tag Groups and Tags topic in this documentation here.
- Configure tags properly - refer to the Configuring Tag Definitions topic in this documentation here.
- Establish proper output formatting - refer to the Configuring Tag Output Formatting topic in this documentation here.
- Understand more about tags in attribute values - refer to
- the Special Character Tags topic (here).
- the Character Tags topic (here).
- the Style Tags topic (here).
- the Hyperlink Tags topic (here).
- Make tags visible in Web UI - refer to the Enable Tag Conversion parameter of the Attribute Value Component topic in the Web User Interfaces documentation here.