The Conditional Attribute Value Metric evaluates the value of a selected attribute based on an operator, and if that evaluation returns as true, then the metric will proceed and evaluate the value of another selected attribute based on an operator. The results of the evaluation (based on the selected operator for the second attribute) are either a '100' (true) or '0' (false).
Important: Metrics are used in conjunction with sufficiencies to determine the quality and completeness of a product's data. While this topic covers the functionality and configuration of the Conditional Attribute Value Metric, it is important that users are also familiar with sufficiencies and how they are combined with metrics. Refer to the Sufficiency Configuration Type topic for information about sufficiencies.
Prerequisites
Before metrics can be created, a Setup Group must be configured to hold them. For information on configuring a setup group for metrics, refer to the Initial Setup for Metrics topic. For information on creating a metric, refer to the Creating and Editing Metrics topic.
Configuration
-
From the Edit Metric Configuration wizard, select 'Conditional Attribute Value Metric.'
-
In the 'If' parameter, click the selector button (
 ) to select the first attribute, select an operator from the operator dropdown menu, and input a value into the 'Value' text field.
) to select the first attribute, select an operator from the operator dropdown menu, and input a value into the 'Value' text field. Repeat these actions for the 'Then' parameter.
Once an operator is selected from the 'Operator' dropdown list, a default error message will appear in the 'Error Message' text field, based on the selected operator.
Operator options include:
-
Is empty - disables the 'Value' text field.
-
Is not empty - disables the 'Value' text field.
-
Equal to
-
Not equal to
-
Contains
-
Regular expression
-
Greater than - only available if the first attribute and/or second attribute has a value that is a number.
-
Less than - only available if the first attribute and/or second attribute has a value that is a number.
-
Length is equal to
-
Length is greater than
-
Length is less than
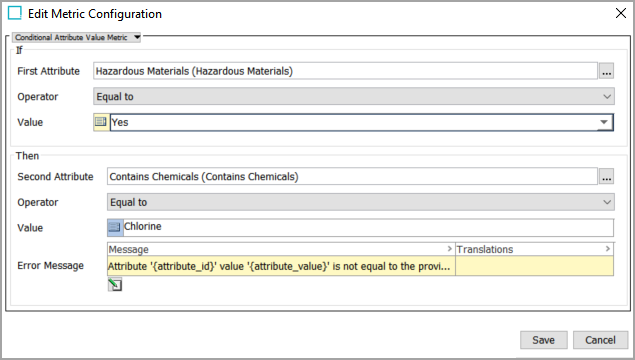
In the example screenshot above, for the 'If' section has 'Hazardous Material' for the first attribute, 'Equal to' for the operator, and input 'Yes' in the 'Value' text field. In the 'Then' section, has 'Contains Chemicals' for the second attribute, 'Contains' for the operator, and input 'chlorine' in the 'Value' text field.
When run, this metric will first check the attribute value for 'Hazardous Material' and if the value is equal to 'Yes,' it will then check the value for the attribute 'Contains Chemicals.' If the attribute value contains the word 'Chlorine,' a score of '100' will be returned. If 'chlorine' is not present in the attribute value, it will return a score of '0' and display a message in the 'Message Preview' text field based on the 'Equal to' operator. If the first attribute 'Hazardous Material' is not equal to 'Yes,' then the metric will not check the value for the second attribute.
Note: If the attribute is not valid for a product, the metric is not applicable for that product and no data quality information will be produced when the Sufficiency Data Calculator event processor is run.
-
-
Click the 'Error Message' editor button (
 ) to display the 'Edit messages' dialog which allows you to edit the error message and/or add additional translations.
) to display the 'Edit messages' dialog which allows you to edit the error message and/or add additional translations. 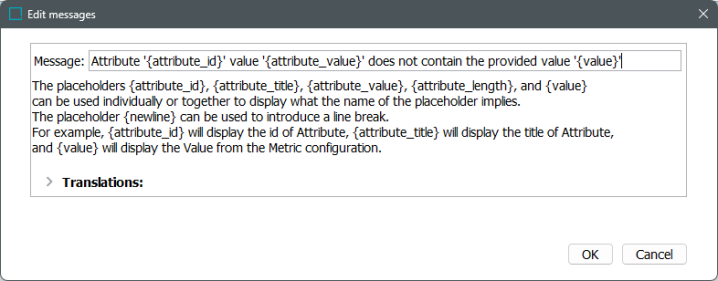
The 'Edit messages' window displays and the 'Message' text field is editable. Descriptive text below the text field describes in detail how the placeholders included in the error message work to create an error message. Although a default error message is suggested, users can edit the error message for the individual need.
Note: Although the error message can be edited by the user, editing the 'attribute_id' and 'attribute_value' placeholders results in a validation error message when attempting to save the edited message. When the metric is run, placeholders are replaced by the 'real values,' e.g., 'attribute_id' would be replaced with the ID of the attribute that the metric is evaluating.
-
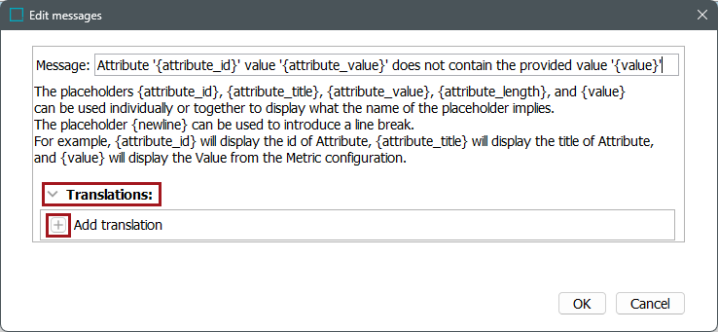
Open the 'Translations' section and click the 'Add translation' button (
 ).
). 
-
Click the 'Language' selector dropdown and choose a language.
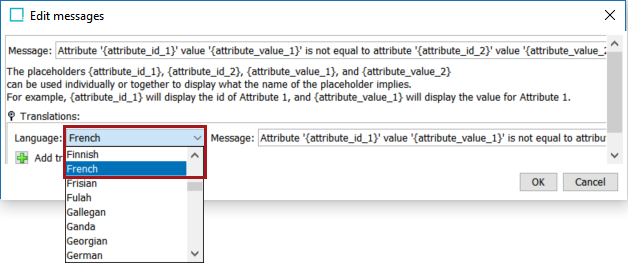
-
In the Message parameter, edit the text to reflect the language specified for translation.
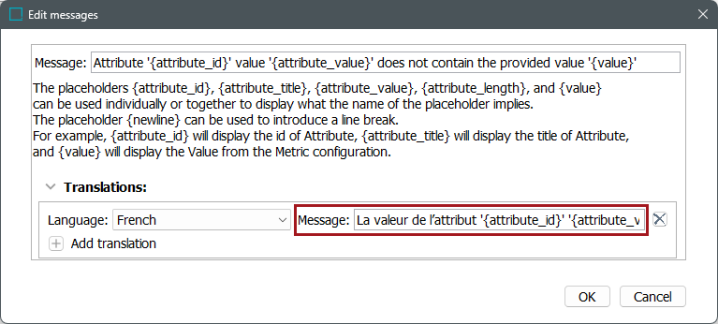
-
Click the 'Add translation' button (
 ) to add another translation or click 'OK' to close the window.
) to add another translation or click 'OK' to close the window. -
Click 'Save' to close the Edit Metric Configuration wizard and save the metric.
Note: Translation error messages are displayed by using locales; they are not context-dependent. For more information about locales, refer to the topic Localization in the Administration Portal documentation. For more information about localized messages, refer to the topic Localized Messages for JavaScript Business Rules in the Business Rules documentation.
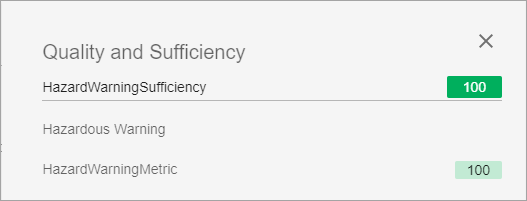
Once the metric is added to a sufficiency and the sufficiency is run, the results are displayed in the sufficiency panel within the Web UI. In the example below, the Conditional Attribute Value Metric (titled 'HazardWarningMetric') has been added to the sufficiency 'HazardWarningSufficiency,' and returned a score of '100' because the attribute 'Hazardous Materials' value is equal to 'Yes' and the attribute 'Contains Chemical' value that contains 'chlorine.' Because the returned score is '100' and not '0,' there is no accompanying error message.
Validation Errors
Validation errors can occur depending on the attribute selected for analysis. A validation error message will occur if:
-
The provided value is not valid based on the selected attribute validation base type.
-
The selected attribute is multivalued.
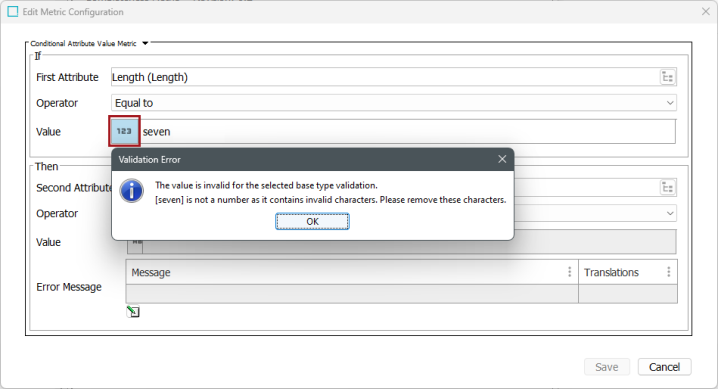
In the example below, the user has input the word 'seven' into the 'Value' text field, but because the attribute selected for analysis has a number validation base type (identified by the highlighted '123'), the provided value must contain numbers only. Because of the incompatibility, a validation error occurs, with an error message that describes the reason for the error.
The following instances will also produce validation errors. However, these errors will not appear until the metric is run. The error message will appear in the Background Process Log of the Data Sufficiency Calculator event processor.
-
A selected attribute has a unit but the value provided by the user in the metric configuration has no unit.
-
A selected attribute has no unit but the value provided by the user in the metric configuration has a unit.
-
A selected attribute and the value provided by the user in the metric configuration have different base unit conversion rules.
-
A selected attribute's unit and/or the value's unit provided by the user in the metric configuration has no base unit conversion rule.
For more information regarding units, including base units and conversion rules, refer to the Units topic in the System Setup documentation