An externally maintained attribute 'lives' outside of STEP because the values are housed in an external system. A typical example is the prices that are maintained in the ERP environment and transferred to STEP for publishing and distribution or addresses maintained in an electronic medical record (EMR). Another example is to use the externally maintained attribute for storing a unique ID (EAN, Manufacturer Part Number, etc.) that is not a STEP ID. It could be generated by other systems like an ERP. An example of externally maintained attributes are 'unique keys'. To know more about unique keys, refer to the Creating and Deleting Keys topic in the System Setup documentation.
For Oracle databases, this action requires single-update mode (SUM), as defined in the Single-Update Mode topic.For Cassandra databases, this action uses Lock-free Schema Change (LFSC) functionality, as defined in the Lock-free Schema Change topic.
Revision Control
Externally maintained attributes are not included in revision control. This means that when a value is imported to one of the workspaces, the new value is automatically applied to all other workspaces. For example, if a supplier enters a value in the 'Main' workspace for an externally maintained attribute, this value is automatically transferred to the other workspaces, e.g., 'Approved'.
When you change an existing internally maintained attribute to an externally maintained attribute (Externally Maintained field changed from No to Yes), you must select the workspace from which values should be taken from and kept on the system. Typically this will be the workspace that contains the most recent updates, e.g., 'Main'.
Note: No revisions are made due to a change on an externally maintained attribute, even if another user modifies it. The data change does generate an event, however, a revision is only generated if some internally maintained attribute is changed.
Sharing LOVs
Externally maintained attributes cannot share LOVs with internally maintained attributes, as values cannot be maintained both internally and externally.
- Setting as externally maintained: If an LOV that is used by any internally maintained attributes is selected, and the attribute is then set as externally maintained, all attributes will become externally maintained.
- Setting as internally maintained: If an LOV that is used by one or more externally maintained attributes is selected, and the attribute is then set as internally maintained, all attributes will become internally maintained.
Setting as Externally Maintained
- In System Setup, expand Attribute Groups, expand the relevant group, and then select the attribute you want to set as externally maintained.
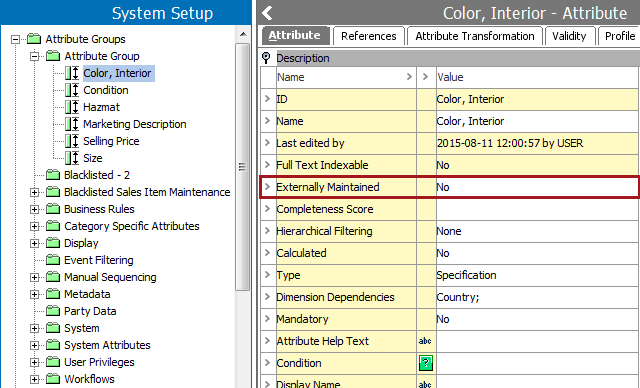
- On the attribute editor > Attribute tab > Description section > double-click the Externally Maintained parameter to display the Externally Maintained dialog.
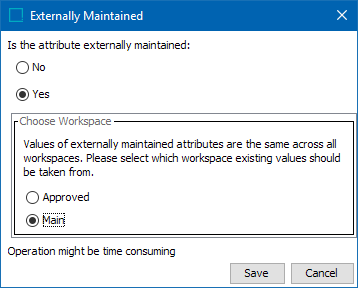
- For 'Is the attribute externally maintained:' radio button, choose Yes to enable the Choose Workspace parameter.
- Select the workspace that contains the existing values that will be used across all workspaces.
- Click Save.
Note: The number of values that already exist for the attribute affects the time required to complete this operation.