Dun & Bradstreet is a leading authority in augmenting and enhancing customer and supplier data with industry leading company information within MDM.
Stibo Systems' MDM includes integration with D&B Match- and D&B Company Profile services.
The D&B Match service integration matches organization master data with D&B’s database of over 265 million organizational records world-wide and return relevant match candidates. Information such as DUNS number, address and contact information and more are provided using the Basic match.
The D&B Company Profile service provides over 220 attributes of business insight related to marketing and sales information, company structures, financial information, key executive contact information and more.
Use Case for Customer MDM
ACME Company is a large, multi-national holding company with subsidiaries that spans across various continents. ACME’s customer portfolio consists of many business-to-business (B2B) accounts which operate across various industries.
In an initiative to improve overall reporting to benefit various departments such as legal, marketing, and finance, ACME realizes a need for a better understanding of their customers. To accomplish this, ACME has commissioned MDM to be the central repository for B2B customer data by sending their customer information from various source systems to MDM for deduplication and further enrichment.
Czarina is a data steward for ACME company, whose responsibilities include ensuring ACME’s master customer data, which drives all reporting and analytics, is accurate and up to date.
Using the Dun & Bradstreet integration offering, MDM firstly obtains the DUNS number for ACME customers using D&B Match by providing basic information such as legal entity name of the organization or a main organization address.
ACME Company’s Stibo Systems' MDM implementation will automatically use the information provided by D&B, to identify duplicate customers and to improve various customer hierarchy structures.
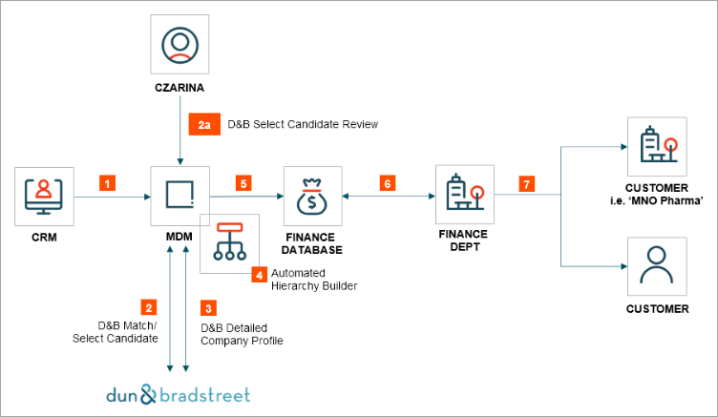
Using the Dun & Bradstreet integration offering, the diagram above depicts the flow of information for this particular use case:
-
Source record information from ACME source system(s) (i.e., CRM) are sent to MDM.
-
As Organization Customer records are created, MDM automatically obtains a DUNS number for the customer(s) by running a D&B Match. The request includes basic information such as legal entity name of the organization, address, phone number, tax identifiers, etc. In response, if D&B returns a match, then a DUNS number is provided and associated with the customer record.
If multiple potential matches are found, D&B will return the list of candidates and require a manual clerical review. It is part of Czarina’s responsibility to review and select the most accurate match; once this is completed the correct DUNS number is associated with the customer record.
Note: The DUNS number is a D&B unique identifier which directly correlates to other government identification protocols such as EIN or Tax Identification Number. This ensures the uniqueness of the customer entity in question.
-
Having obtained the DUNS number, ACME will further enrich their B2B customer data by automatically leveraging the D&B Detailed Company Profile integration.
As a global company that operates across multiple industries, ACME plans to utilize this detailed information to build an industry segmentation hierarchy for their customers, which allows the finance department to properly report on, invoice, as well as be made aware of any relevant tax breaks associated to customers within industries.
-
A separate process within MDM is created to automate the creation of industry hierarchies and categorization of customers within such hierarchies. This logic is based on D&B profile data and must execute after D&B Detailed Company Profile enrichment.
-
Once the relevant hierarchy(s) is created, data is then synchronized with external systems (i.e., Finance database) (refer to details below)
-
From there, the Finance department now has the complete view of their customers with respect to their particular industry and available metadata.
-
The Finance department now can confidently send appropriate invoices and other business transactions.
Use Case for Supplier MDM
ACME Company is a large manufacturer who relies on a large network of suppliers for their raw materials and finished goods.
As part of a company-wide initial to reduce cost both from ACME buy-side and sell-side operations, Arthur, who is on the procurement team and is responsible for managing supplier relations, must be able to leverage third-party Dun & Bradstreet data to identify cost-cutting opportunities.
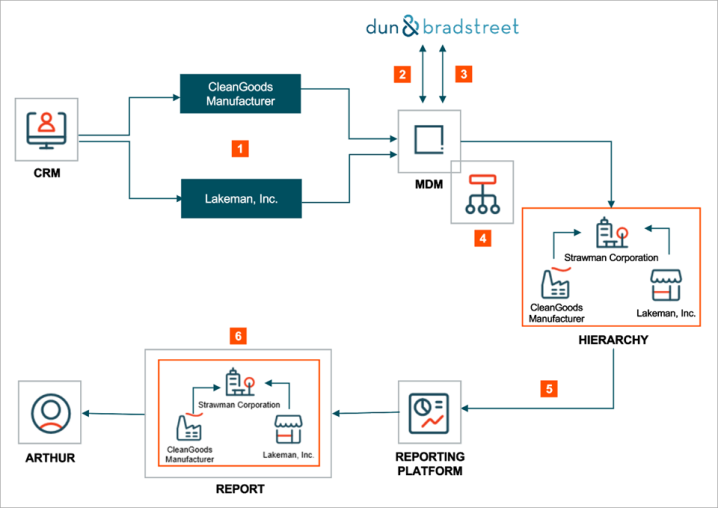
Using the Dun & Bradstreet integration offering, the diagram above depicts the flow of information:
-
Supplier record information from ACME source system(s) (i.e., CRM) are sent to MDM.
-
As Supplier records are created, MDM automatically obtains a DUNS number for the suppliers by running a D&B Match. The request includes basic information such as legal entity name of the supplier, address, phone number, tax identifiers, etc. In response, if D&B returns a match, then a DUNS number is provided and associated with the supplier record.
If multiple potential matches are found, D&B will return the list of candidates and require a manual clerical review. It is part of an MDM Specialist’s responsibility to review and select the most accurate match; once this is completed the correct DUNS number is associated with the supplier record.
Note: The DUNS number is a D&B unique identifier which directly correlates to other government identification protocols such as EIN or Tax Identification Number. This ensures the uniqueness of the customer entity in question.
-
Having obtained the DUNS number, ACME will further enrich their supplier data by leveraging the D&B Detailed Company Profile integration.
-
A separate process within MDM is created to automate the creation of legal hierarchies. This logic is based on various DUNS numbers within D&B profile data and must execute after D&B Detailed Company Profile enrichment.
-
Once the legal hierarchy(s) is created, data is then synchronized with external systems (i.e., reporting platform).
-
From there, Arthur may now obtain reports that contain the relevant supplier master data and all the relationships provided by Dun & Bradstreet.
As a global company that operates across multiple industries, ACME plans to utilize this detailed information to build legal hierarchical representations of their existing suppliers’ relationships. This allows Arthur to ascertain new suppliers to source and leverage existing relationships to negotiate for lower pricing.
Creation of Hierarchies
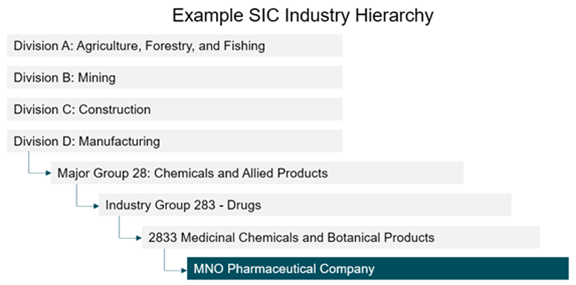
Once organization records have been enriched with D&B data, a separate process is initiated to evaluate SIC and NAICS industry codes to automate the building of an industry hierarchy as well as categorization of customers into this hierarchy.
Identifying More Duplicates
As ACME’s MDM solution is configured to match customer records on various data provided by D&B, whenever it is available, event triggering of matching algorithms, will automatically identify and merge duplicate entity records that could not previously be identified, due to a lack of common identifiers on the duplicate records.
For further information on MDM’s matching capabilities, refer to the Matching, Linking, and Merging documentation.
D&B Data Flow within MDM Application
The progression of data flow for B2B entity records as it is de-duplicated within MDM and also further enriched via Dun & Bradstreet is shown below.
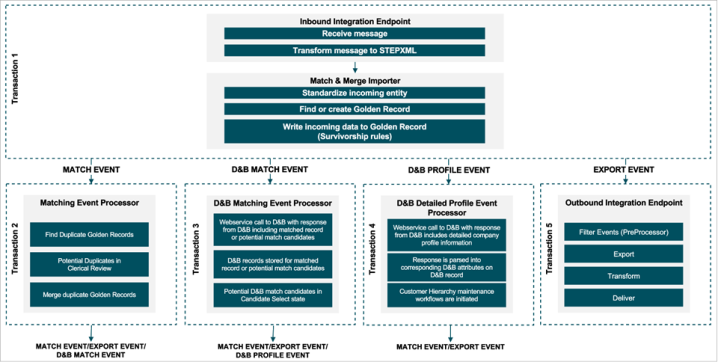
Transaction 1: Inbound Integration Endpoint
An inbound integration endpoint will receive a message and transform it into STEPXML.
Once transformed, the Match & Merge Importer will:
- Execute standardizations and other associated business rules to cleanse the data. Cleansed data allows for the Match algorithm to more accurately identify duplicate records.
- Determine the target Golden Record. For more information, refer to the IIEP - Configure Match and Merge Importer Processing Engine topic of the Data Exchange documentation.
- Survivorship rules will write any updates from the incoming data to the golden record. For more information, refer to the Golden Records Survivorship Rules topic of the Matching, Linking, and Merging documentation.
- To the extent that a Golden Record was created, or an existing Golden Record was updated, events are written to event queues triggering on those changes. In this case, a Matching event processor as well as an Outbound Integration Endpoint.
Transaction 2: Matching Event Processor
When new golden records are created or an existing golden record is updated, this will trigger a matching event, with the purpose of comparing golden records to each other. Prior to matching, the golden record under treatment will have its match codes updated.
Matching golden records may result in a clerical review workflow initiation or a merge, depending on the score. Additionally, survivorship rules should trigger a D&B Match event
For more information, refer to the Match and Merge Clerical Review - Merge topic of the Matching, Linking, and Merging documentation.
Transaction 3: D&B Match Event Processor
Golden record events are then triggered for the D&B Match event processor. This triggers a web service call to D&B to obtain a corresponding match to existing entities within D&B database. The D&B response will invoke one of two types of behaviors within MDM.
If a direct match is found, a corresponding D&B entity record is created within MDM and referenced to the golden organization record. Attribute information from the D&B response are then parsed into D&B attributes.
Once a DUNS number is obtained, a D&B Profile event should be triggered for the D&B Detailed Profile Event Processor.
If potential match candidates are returned by D&B, then corresponding D&B entities are created and submitted to the 'Select Candidate' workflow state.
Transaction 4: D&B Profile Event Processor
Once a D&B match has been found, a second D&B event processor sends the D&B record with its corresponding DUNS number back to D&B for retrieval of detailed company profile information.
The D&B response from this call is then parsed into corresponding D&B attributes on the D&B record.
Once a D&B response is received and parsed, two events should be triggered:
- Match Event – in the case that the detailed profile provides more information that may affect matching results, the Matching Event Processor is invoked to re-run the match algorithm.
- Export Event – to synchronize the golden record information with external systems, an export event is triggered for an Outbound Integration Endpoint(s)
Transaction 5: Outbound Integration Endpoint
Whenever Golden Records are created or changed, an export event will trigger. This allows the mastered data to be synced back to the various source systems.
For more information, refer to the Outbound Integration Endpoints topic of the Data Exchange documentation.