A new revision is not created for every change to an object, thus STEP does not have traceability on the field level. This means that not all historical values on an object are stored as they may have differed between revisions, and the values are only stored at revisions. If the same user is making continuous edits to an object, these are not captured as a revision until the object is approved, the automatic revision threshold expires, or another user makes changes to the object.
For more information, refer to the Important considerations for revisions section below.
A revision can be created in the following ways:
- Automatically upon creation of a new workspace revisable object.
- Automatically upon approval of a workspace revisable object.
- Automatically each time a change is made by a different user, or when any change is made following an approval. For assets, when the digital media file associated with an asset in STEP is changed, this generates a revision on the asset object.
- Automatically when a user makes a change and the current revision is older than a configurable threshold, even if the same user also made the previous change. For more information, refer to the Timing for Automatic Revisions topic here.
- Manually, from Maintain menu > Make Revision. Enter a comment and click OK. Manual revisions are also referred to as a major revision.
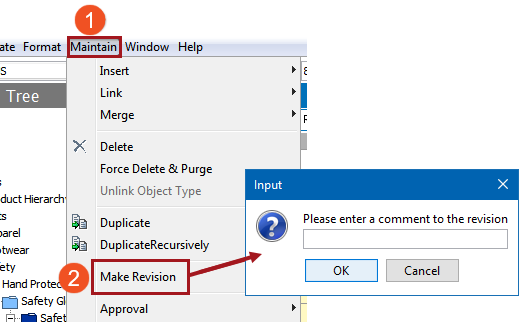
Note: Revisions can be created when the data is perfect, in preparation for future unexpected changes. Creating a manual revision allows you to revert back to perfect data. Manual creation of revisions must be done for one node at a time; it is not possible to create revisions manually in bulk.
Important considerations for revisions
- Externally maintained data and calculated data are exceptions to the revision generation options mentioned. Changes to the value of an externally maintained or calculated attribute value on an object do not generate a revision for that object, do not change the approval status for the object, and are not retained as part of the revision history of the object.
- When objects that are part of the revision history for another object are deleted, these are not retained with the revision history. For example, if an object had an attribute value populated at the time of a revision, and subsequently that attribute is deleted from STEP, reverting to the previous revision will not include a value for that attribute as the attribute no longer exists. Among other examples, the same applies for workflows that included business rules that are subsequently deleted, objects that referenced other objects or assets that were subsequently deleted, or reference and link types when deleted.