Character tags are not paired, meaning that they do not require a opening and closing tag. For all character tags, the character(s) entered in the Rendering parameter display in the workbench GUI with a gray background. For example,  .
.
Because there are several thousand special characters available on many different types of fonts, it may be necessary to create a tag name (such as 'telephone'), then access that specific character in that font in the character conversion table. Consult the web for more available special characters.
Note: When importing tags into STEP, the syntax must conform with STEP protocol. Valid formatted STEP tags allow data to be imported correctly.
< and > Characters
Recommended practice is to set up tag entries for 'less than' <lt/> and 'greater than' <gt/> characters along with their rendering. This enables a user to enter the < or > directly on the keyboard. STEP will take this single keystroke and immediately converts that to the STEP tag <lt/> or <gt/>, and shows in the workbench as the single character (background of gray). However, this is only useful for those cases where a user wishes to display the characters of greater than or less than as a symbol within a attribute values. Example: >40mg
Although the < and > characters are allowed in an object ID, it is not recommended practice. If these character tags are entered within an object's name, STEP allows them and saves them as the STEP character tags <lt/> and <gt/>. However, this may cause confusion when using the Search or Advanced Search functions in STEP. Additionally, if data is imported via an XLS file, and these characters are used in the object names, the system throws an error, though it will still load the data and will transform the < and > characters to an <lt/> or < gt/>.
Important: In the STEP UI, do not type a STEP tag directly, such as <bold>. STEP converts the less than (<) and the greater than (>) characters into separate tags instead of applying a style of bold to a string of text. The correct approach is to apply the specific function for inserting the appropriate character tag.
Importing < and > Characters
Importing the 'less than' and 'greater than' characters successfully depends on the format being used. Improperly formatted tags can result in unexpected results including warnings in the BGP Execution Report or ignored characters.
Importing an XML format requires the following:
-
<lt/> indicates the 'less than' tag (<)
-
<gt/> indicates the 'greater than' tag (>)
Importing a non-XML format requires the following:
-
<lt/> indicates the 'less than' tag (<)
-
<gt/> indicates the 'greater than' tag (>)
& and " Characters
The & (ampersand) and the " (double straight quote) characters are 'automatic' when converting to on output. An accepted industry standard is to use the & and " when these characters occur in a text stream in XML.
However, do not enter & and " directly into STEP attribute values in the workbench or Web UI as it does not give the desired results. Instead, enter & and " directly from the keyboard.
Insert a Character Tag
Use the following steps to implement a character tag.
-
In an attribute value field, position the cursor where the special character should be placed.

-
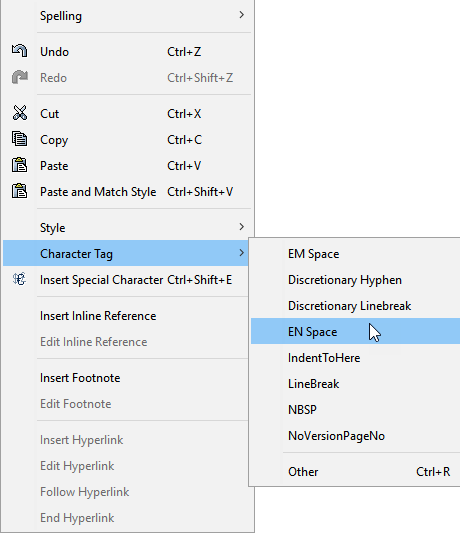
Right-click and choose the Character Tag option.
-
A list of recently used character tags displays for selection.
-
If the desired character tag is not in the list, click Other, and the Insert Character Tag dialog displays, showing a complete list of all character tags created in the system.
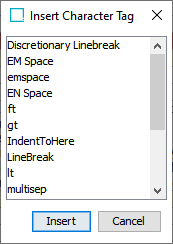
Select the desired character tag from the Insert Character Dialog, and click Insert.
The tag is applied and visible in the editor.

-