This section provides a process overview of the primary data flow throughout the STEP system using a Consolidation and Coexistence approach.
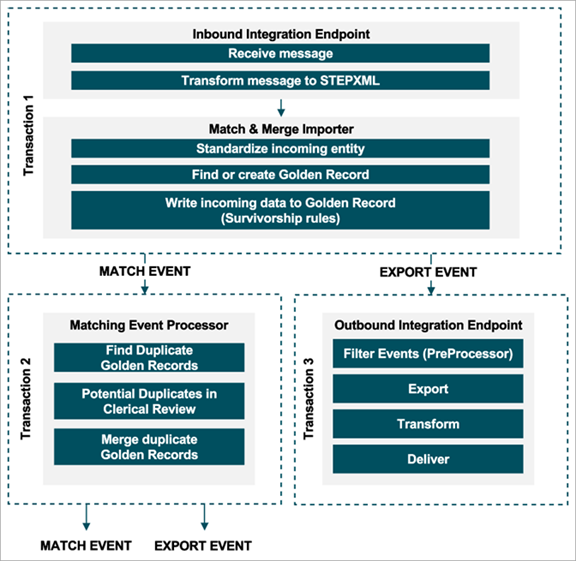
Transaction 1: Inbound Integration Endpoint
An inbound integration endpoint will receive a message and transform it into STEPXML.
Once transformed, the Match & Merge Importer will:
- Execute standardizations and other associated business rules to cleanse the data. Cleansed data allows for the Match algorithm to more accurately identify duplicate records.
- Determine the target Golden Record. For more information, refer to the IIEP - Configure Match and Merge Importer section of the Data Exchange documentation here.
- Survivorship rules will write any updates from the incoming data to the golden record. For more information, refer to the Golden Records Survivorship Rules section of the Matching, Linking, and Merging documentation.
- To the extent that a Golden Record was created, or an existing Golden Record was updated, events are written to event queues triggering on those changes. In this case, a Matching event processor as well as an Outbound Integration Endpoint.
Transaction 2: Matching Event Processor
When new golden records are created or an existing golden record is updated, this will trigger a matching event, with the purpose of comparing golden records to each other.
Prior to matching, the golden record under treatment will have its match codes updated.
Matching golden records may result in a clerical review workflow initiation or a merge, depending on the score.
For more information on Clerical Reviews, refer to the Clerical Review section of the Matching, Linking, and Merging documentation.
Transaction 3: Outbound Integration Endpoint
Whenever Golden Records are created or changed, an export event will trigger. This allows the mastered data to be synced back to the various source systems.
For more information about Outbound Integration Endpoints, refer to the Outbound Integration Endpoint section of the Data Exchange documentation here.
Note: Clerical Review is not a blocking state.
Use Case 1: New Golden Record
- Transaction 1: Import
- IIEP: Receive message
- IIEP: Transform message to STEPXML
- M&M: Standardize Address
- M&M: Check if Source System and Source Record ID is associated to existing, active Golden Record (it is not)
- M&M: Generate Match codes for incoming data and look for matching record using Match Code and Matching Algorithm (no match is found)
- M&M: Create new Golden Record
- M&M: Survivorship Rules Write data to new Golden Record
- Transaction 2: Handle duplicate Golden Records
The Matching Event Processor polls for events on a schedule.
- Update match codes for changed Golden Record and look for matching Golden Records using Match Code and Matching Algorithm
- No duplicate golden records found
- No potential duplicate golden records found
3. Transaction 3: Export
Outbound integration endpoints poll for events on a schedule. Notice that transaction 2 and 3 are independent.
- OIEP: No event PreProcessor in use
- OIEP: Export data to STEPXML
- OIEP: Transform to target message format
- OIEP: Deliver message to target
Use Case 2: Update Existing Golden Record with Known Source Record ID
- Transaction 1: Import
- IIEP: Receive message
- IIEP: Transform message to STEPXML
- M&M: Standardize Address
- M&M: Check if Source System and Source Record ID is associated to existing, active Golden Record (it is)
- M&M: Survivorship Rules Write data to existing Golden Record
- Transaction 2: Handle Duplicate Golden Records
The Matching Event Processor polls for events on a schedule.
- Update match codes for changed Golden Record and look for matching Golden Records using Match Code and Matching Algorithm
- If an absolute match is found, auto-merge
- MA: Survivorship Rules Write data to existing Golden Record
- If potential duplicate golden records are found, initiate into clerical review
- Transaction 3: Export
Outbound integration endpoints poll for events on a schedule. Notice that transaction 2 and 3 are independent.
- OIEP: No event PreProcessor in use
- OIEP: Export data to STEPXML
- OIEP: Transform to target message format
- OIEP: Deliver message to target
Use Case 2.1: Update Existing Golden Record with Known Golden Record ID
- Transaction 1: Import
- IIEP: Receive message
- IIEP: Transform message to STEPXML
- M&M: Standardize Address
- M&M: Find existing Golden Record based on STEP ID (golden record id)
- M&M: Survivorship Rules Write data to existing Golden Record
- Transaction 2: Handle Duplicate Golden Records
The Matching Event Processor polls for events on a schedule.
- Update match codes for changed Golden Record and look for matching Golden Records using Match Code and Matching Algorithm
- If an absolute match is found, auto-merge
- MA: Survivorship Rules Write data to surviving Golden Record
- If potential duplicate golden records are found, initiate into clerical review
- Transaction 3: Export
Outbound integration endpoints poll for events on a schedule. Notice that transaction 2 and 3 are independent
- OIEP: No event PreProcessor in use
- OIEP: Export data to STEPXML
- OIEP: Transform to target message format
- OIEP: Deliver message to target
Use Case 3: Add new source record to existing golden record by matching
- Transaction 1: Import
- IIEP: Receive message
- IIEP: Transform message to STEPXML
- M&M: Standardize Address
- M&M: Check if Source System and Source Record ID is associated to existing, active Golden Record (it is not)
- M&M: Generate Match codes for incoming data and look for matching record using Match Code and Matching Algorithm (match is found)
- M&M: Update Existing Golden Record with additional source record ID
- M&M: Survivorship Rules Write data to existing Golden Record
- Transaction 2: Handle Duplicate Golden Records
The Matching Event Processor polls for events on a schedule.
- Update match codes for changed Golden Record and look for matching Golden Records using Match Code and Matching Algorithm
- If an absolute match is found, auto-merge
- MA: Survivorship Rules Write data to surviving Golden Record
- If potential duplicate golden records are found, initiate into clerical review
- Transaction 3: Export
Outbound integration endpoints poll for events on a schedule. Notice that transaction 2 and 3 are independent.
- OIEP: No event PreProcessor in use
- OIEP: Export data to STEPXML
- OIEP: Transform to target message format
- OIEP: Deliver message to target
Use Case 3.1: Add New Source Record to Existing Golden Record by Golden Record ID
This use case is relevant when the Find Similar web service has been used to identify that a golden record for a specific entity already exists and a new source record needs to be associated with it.
- Transaction 1: Import
- IIEP: Receive message
- IIEP: Transform message to STEPXML
- M&M: Standardize Address
- M&M: Find existing Golden Record based on STEP ID (golden record id)
- M&M: Update existing Golden Record with new source record ID
- M&M: Survivorship Rules Write data to new Golden Record
- Transaction 2: Handle Duplicate Golden Records
The Matching Event Processor polls for events on a schedule.
- Update match codes for changed Golden Record and look for matching Golden Records using Match Code and Matching Algorithm
- If an absolute match is found, auto-merge
- MA: Survivorship Rules Write data to surviving Golden Record
- If potential duplicate golden records are found, initiate into clerical review
- Transaction 3: Export
Outbound integration endpoints poll for events on a schedule. Notice that transaction 2 and 3 are independent.
- OIEP: No event PreProcessor in use
- OIEP: Export data to STEPXML
- OIEP: Transform to target message format
- OIEP: Deliver message to target
Use Case 4: Add New Source Record to Existing Golden Record by Matching, Clerical Review
- Transaction 1: Import
- IIEP: Receive message
- IIEP: Transform message to STEPXML
- M&M: Standardize Address
- M&M: Check if Source System and Source Record ID is associated to existing, active Golden Record (it is not)
- M&M: Generate Match codes for incoming data and look for matching record using Match Code and Matching Algorithm
- M&M: Match Rules will not find certain matches
- M&M: Create new Golden Record
- M&M: Survivorship Rules Write data to new Golden Record
- Transaction 2: Handle Duplicate Golden Records
The Matching Event Processor polls for events on a schedule.
- Update match codes for changed Golden Record and look for matching Golden Records using Match Code and Matching Algorithm
- Identify that newly created golden record is within clerical review threshold and put oldest record in clerical review workflow
- Transaction 3: Merge
- User review duplicate records in clerical review
- User merge potential duplicates
- Source record references from non-surviving record gets written to surviving record
- References TO the non-surviving record gets moved to the surviving record
- Survivorship rules promote updates from non-surviving- to surviving golden record
- Non-survivor gets deactivated and Merged-Into reference is established from non-survivor to survivor
- Transaction 4: Export
The deactivated record is exported, as the 'Merged-Into' reference was added and the 'Is Deactivated' was changed to 'true'. The surviving record is exported, as source records were added to it. Any other object having a reference target moved from the non-surviving record to the surviving record will get exported, to the extent triggering definitions are defined for it.
- OIEP: No event PreProcessor in use
- OIEP: Export data to STEPXML
- OIEP: Transform to target message format
- OIEP: Deliver message to target
Use Case 5: Manually Modify Golden Record
- Transaction 1: Manual Edit
- Data Steward: Manually makes edits on an existing Golden Record via the Web UI.
- Transaction 2: Handle Duplicate Golden Records
The Matching Event Processor polls for events on a schedule.
- Update match codes for changed Golden Record and look for matching Golden Records using Match Code and Matching Algorithm
- If an absolute match is found, auto-merge
- MA: Survivorship Rules Write data to existing Golden Record
- If potential duplicate golden records are found, initiate into clerical review
- MA: If match is confirmed, survivorship Rules Write data to existing Golden Record
- MA: If match is rejected, create a ‘Confirmed Non-Duplicate’ reference between the two (or more) Golden Records.
- Transaction 3: Export
Outbound integration endpoints poll for events on a schedule. Notice that transaction 2 and 3 are independent.
- OIEP: No event PreProcessor in use
- OIEP: Export data to STEPXML
- OIEP: Transform to target message format
- OIEP: Deliver message to target
Use Case 6: Import Cross References by Source Record ID
- Transaction 1: Import
- IIEP: Receive message
- IIEP: Transform message to STEPXML
- M&M: Standardize Address
- M&M: Check if Source System and Source Record ID is associated to existing, active Golden Record (it is for the target entity)
- M&M: Generate Match codes for incoming data and look for matching record using Match Code and Matching Algorithm
- M&M: Match Rules will not find certain matches
- M&M: Create new Golden Record (Source entities)
- M&M: Survivorship Rules Write data to new Golden Record including creating cross references
- Transaction 2: Handle Duplicate Golden Records
The Matching Event Processor polls for events on a schedule.
- Update match codes for changed Golden Record and look for matching Golden Records using Match Code and Matching Algorithm
- If an absolute match is found, auto-merge
- MA: Survivorship Rules Write data to surviving Golden Record
- If potential duplicate golden records are found, initiate into clerical review
- Transaction 3: Export
Outbound integration endpoints poll for events on a schedule. Notice that transaction 2 and 3 are independent.
- OIEP: No event PreProcessor in use
- OIEP: Export data to STEPXML
- OIEP: Transform to target message format
- OIEP: Deliver message to target
When the Match and Merge Importer reads cross references in the STEPXML, the target Entity may be specified with a source system and a source record ID, instead of a STEP ID. This allows import of references to objects, where the STEP ID is not known.