In a centralized implementation methodology, origination and stewardship / maintenance of entity records reside within MDM. While many different types of data are often associated with entity records, it is important to note that the role of MDM is to capture the customer master data that drives operational processes within an organization. Within this section, we will focus primarily on centralized methodology for Business-to-Business (B2B) organizations within the Consumer Packaged Goods (CPG) industry.
CPG companies source from a multitude of suppliers to manage a wide array of products, brands, categories, and channels, while serving diverse customer segments across multiple geographic regions worldwide. Their end consumers of products are either individual consumers or other businesses such as hospitals, schools, restaurants, etc.
While a major business cost is the procurement of raw materials, goods, and services from various suppliers, most of the revenue is generated by selling through a network of retail chains, distributors, and master wholesalers. These parties are who the CPG company considers its customers. Any CPG company has the following operational functions as part of the sales side of their business:
- Sales
- Distribution
- Accounting and finance
To meet the needs of such operational functions, MDM is implemented to enforce and guide the organization in onboarding suppliers and/or customers by providing a means to enrich, govern, and maintain their entity data in a centralized manner.
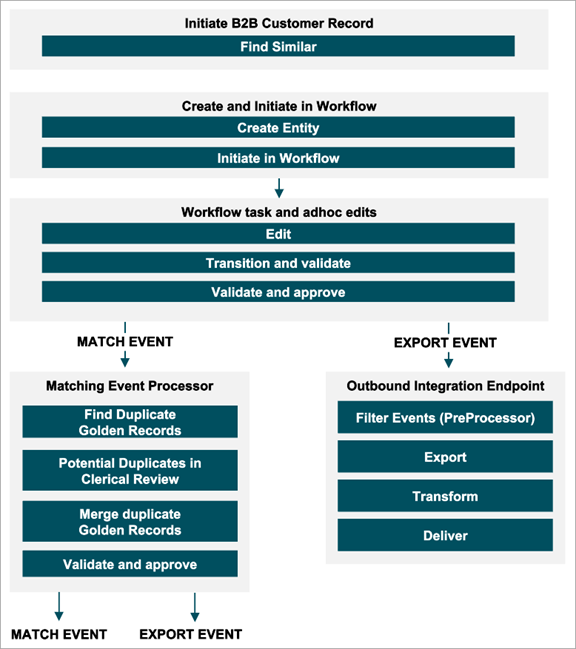
Initiate B2B Customer Record
A new supplier entity record request is initiated within MDM through the Web UI interface. Initial minimal data provided may include the legal name of the entity being onboarded. At this point, two options are provided in the Web UI:
- Find Similar – to ensure no other record with a similar legal name already exists, the user is presented with matching candidates if any are found.
- Save – If no matching candidate is found, the user may save as a new record.
For details on Find Similar, refer to the Find Similar topic in the Web User Interfaces documentation here.
Create and Initiate in Workflow
Once a record is created, it is automatically initiated into a workflow.
Workflow Task and Ad Hoc Edits
By leveraging STEP Workflows, the operational processes such as onboarding, enrichment, and maintenance of master data may be closely owned by various departmental stakeholders across the organization.
The onboarding workflow allows for detailed enrichment of the new entity record as well as various business conditions to ensure data integrity is upheld.
Users may be presented with the following options:
- Save – Edits made to the new record may be saved. It is not uncommon that the save button executes data verification business action(s), such as address verification.
- Submit – Saved edits to a new record may then be submitted to the next state of the workflow. Data validation may also take place on submission to the next state.
- Delete – User has the option to delete the new record if necessary.
For more information, refer to the Workflows in Web UI topic in the Web User Interfaces documentation here.
Note: All user actions available are dependent upon the user privileges afforded to said user. It is recommended that privileges are afforded to users based on their role. For example, a logistics specialist cannot delete a record. Only the MDM Specialist or some other system administrative role can be granted all privileges. For more information, refer to the Privilege Rules topic in the System Setup documentation here.
For ad hoc edits, like edits to an existing record outside of a workflow, the user is presented with the following options:
- Save – Edits made to the new record may be saved. It is not uncommon that the save button executes data verification business action(s), such as address verification. Data validation may also take place at this point to ensure data integrity is upheld.
- Request Approval – Approval of changes to the entity record should be the responsibility of the MDM Specialist. This action will initiate the record into an Approval workflow for the approval. Further data validations may take place within this workflow to ensure data integrity.
Upon final approval of the entity record, a match event is generated for the matching event processor to execute matching with the newly created record.
Approved Workspace
Data promoted to the approved workspace should be considered as having been validated and completed. Approved entity data may be synchronized to a downstream system to drive external business processes and/or analytics.
Matching Event Processor
Whenever entity records are approved, this will trigger a match event. The event will trigger the match algorithm to execute and compare the new or existing golden record with the entire dataset of entity records.
Prior to matching, the entity record under treatment will have its match codes updated. During matching, data within the Approved workspace is to be evaluated. At this juncture, there are two solution paths that may be taken; the decision of which should be determined using the business requirements gathered by the implementation team.
Merge and Auto-Approve Matches
In the event that a resulting match score is above the auto-merge threshold, candidates are merged by the system. Survivorship rules will update the merged record within the Main workspace and auto-approve the changes to promote to the Approved workspace.
There may still be a clerical review threshold should it be dictated by the business requirements.
Review all Matches
All match scores above a certain threshold are considered as potential matches and candidates are manually reviewed. Survivorship rules will auto-initiate the potential candidates into an Approval / Clerical Review workflow to be reviewed by an MDM specialist.
Match scores that fall beneath a certain threshold may be automatically considered as non-matches.
Outbound Integration Endpoint
Whenever entity records are approved, an export event will trigger. This allows the mastered data to be synchronized with various downstream systems.