A gateway integration endpoint (GIEP) allows STEP to communicate with the external storage system. Once a gateway integration endpoint has been created and the external system (Amazon S3 Blob Storage, Microsoft Azure Blob Storage, or REST) has been selected, the configuration settings allow you to identify the server housing the required data.
The following steps are for Microsoft Azure Blob Storage configuration.
Prerequisites
In order to use the Gateway Integration Endpoint Configuration dialog, the following server configuration properties must be set up first.
Note: Sensitive configuration values that will be filtered from view are denoted with 'Secret.' This means that the actual values will not be visible to users or to Stibo Systems, for example, via Admin Portal configuration lists and remote diagnostics.
-
Connection Info
The syntax for specifying the connection details is:
BlobStorage.Azure.Secret.Connection.1=<connection-string-alias>,<azure-connection-string>
BlobStorage.Azure.Secret.Connection.2=<connection-string-alias2>,<azure-connection-string2>
The <connection-string-alias> and <connection-string-alias2> will be displayed in the ‘Connection Info’ dropdown menu for the Gateway Integration Endpoint (explained in the next section), showing the alias instead of the actual connection string value.
More information about connection string values and how to find or create them can be found online at https://portal.azure.com (go to Storage Accounts >> Your-Storage- Account >> Access Key >> Connection String).
-
Container Name
The syntax for specifying the container name is:
BlobStorage.Azure.Secret.ContainerName.1=<my-container-name> BlobStorage.Azure.Secret.ContainerName.2=<my-other-container-name>
The <my-container-name> and <my-other-container-name> will be displayed in the ‘Container Name’ dropdown menu for the Gateway Integration Endpoint (explained in the next section).
Note: Two of each property are shown above; however, you can have numerous config properties by increasing the number at the end (e.g., .1, .2, .3, etc.).
Example configuration:
BlobStorage.Azure.Secret.Connection.1=AzureConn,DefaultEndpointsProtocol=https;AccountName=pimtest;AccountKey=t/mGLRrqkX64WM0yBdIp4qEMHELl0Y933zVDuKHz+/vBC20wRud3GXstYaxKqk1yF9C3D9d/AZbJ+AStTVkmlA==;EndpointSuffix=core.windows.net
BlobStorage.Azure.Secret.ContainerName.1=besiProducts
It is also possible to use a Shared Access Signature (SAS) credential for the ConnectionString.
The SAS token must be created directly on the blob storage account itself (and not the corresponding container); and as a minimum, it must have Service, Container, and Object specified as its 'Allowed resource types' as well as Read, Write, and List for its 'Allowed permissions' to grant the proper access rights to STEP.
These resource types and permissions are required to allow STEP to perform all the needed operations to deliver the content (blobs) to the specified Azure Blob Storage account's container.
Important: If the SAS token has insufficient privileges, the delivery will result in an error message similar to this one:
If you are using a SAS token, and the server returned an error message that says 'Signature did not match', you can compare the string to sign with the one generated by the SDK. To log the string to sign, pass in the context key value pair 'Azure-Storage-Log-String-To-Sign': true to the appropriate generateSas method call. Remember to disable 'Azure-Storage-Log-String-To-Sign' before going to production as this string can potentially contain PII.
Status code 403, "<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?><Error><Code>AuthorizationResourceTypeMismatch</Code><Message>This request is not authorized to perform this operation using this resource type. RequestId:836910b1-801e-001a-4da2-900fc9000000 Time:2022-07-05T19:11:07.4796215Z</Message></Error>"
An example using a SAS configuration is below:
BlobStorage.Azure.Secret.Connection.2=AzureConnSAS,BlobEndpoint=https://pimtest.blob.core.windows.net/;SharedAccessSignature=sv=2021-06-08&ss=b&srt=sco&sp=rwlx&se=2023-01-01T05:00:00Z&st=2022-07-05T18:58:41Z&spr=https&sig=N5X7J9tCMscbOTYioR4sb30H7B%2B0j8dk74MSCQ6Gxsw%3D
BlobStorage.Azure.Secret.ContainerName.2=besiProducts
Configuring the Gateway Integration Endpoint
Once the properties as described above are entered into the sharedconfig.properties file, the options outlined within these properties will display in the dropdowns in the configuration dialog. If the dropdowns are empty, then the properties are not set up or set up incorrectly.
-
On the Gateway Integration Endpoint Configuration dialog, use the following parameters to specify which external system the gateway integration endpoint will access.
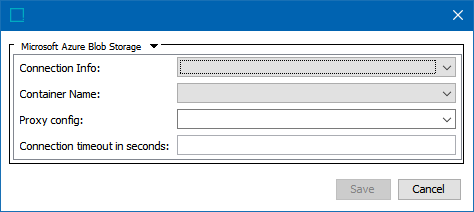
- Connection Info - The desired Azure connection.
- Container Name - The Azure container name to use.
- Proxy config - Select the desired HTTP proxy configuration if the delivery connection must first pass through a proxy server with its own login requirement.
- Connection timeout in seconds - The connection timeout on the request in seconds. If left blank, the driver default will be used.
Note: For more information regarding proxy configurations, refer to the topic HTTP Proxy Configurations in the Data Exchange documentation here.
-
Click Save to complete the configuration.
Using the Gateway Integration Endpoint
Configuration of a GIEP is required to set up an / a:
-
Asset Publisher Event Processor:
For more information, refer to the Asset Publisher Processing Plugin Parameters and Triggers topic in the Event Processors section of System Setup documentation here.
-
Cloud Blob Storage Delivery Method:
For more information, refer to the Cloud Blob Storage Delivery Method topics in the OIEP Delivery Methods (here) and the Export Manager Delivery Methods (here) sections of the Data Exchange documentation.