JavaScript-based business rules can be created, maintained, and tested outside STEP. This allows customers and partners to govern the lifecycle of business rules in a standard source code control system such as Git, and from there, be able to deploy appropriate versions of the business rules to the various STEP systems that are part of a Development, Testing, Acceptance, and Production (DTAP) environment.
This topic describes the following in detail:
-
Editable Business Rule Format
-
Options for Export
-
Options for Import
-
REST Resources for Testing and Validation
Note: The 'configuration-management' add-on component must be activated to enable the functionality described below.
Business rules can be exported as *.js files that can be edited outside STEP and imported back into a STEP system, creating or updating a business rule. This format is available for business conditions, actions, functions, and libraries of 'Global' scope created using the business rule format introduced with STEP 7.0. Each file represents a single business rule and contains all information necessary to create / update the rule on import.
In the *.js files, metadata and definitions of non-JavaScript operations and preconditions ('Applies if') is output in comment sections, while the JavaScript for the individual operations and preconditions are wrapped in functions with objects provided by the execution context as parameters (binds, messages, function input parameters, and referenced libraries).
For example, assume there is a simple business action with one JavaScript operation and a non-JavaScript precondition as shown below:
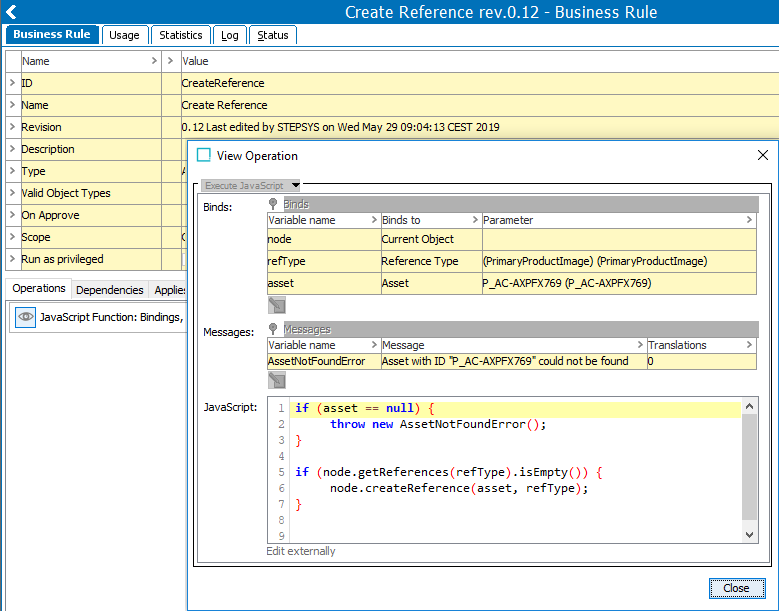
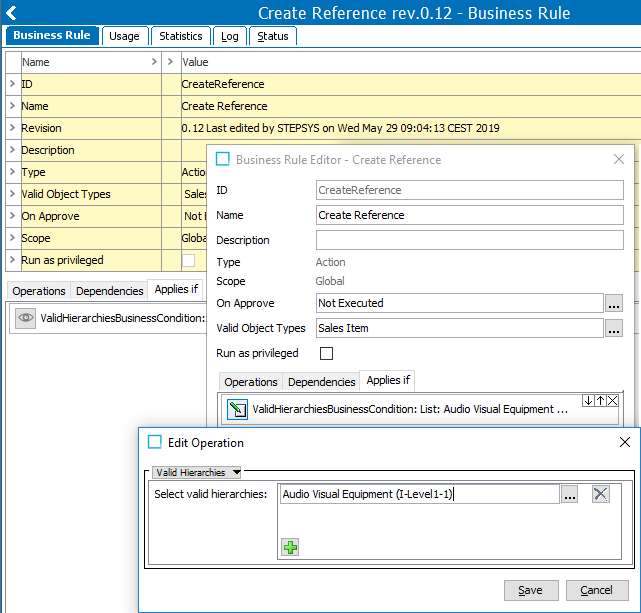
When exported using the default settings, the business action are represented in the generated file as follows:
/*===== export metadata =====
{
"contextId" : "Context1",
"workspaceId" : "Main"
}
*/
/*===== business rule definition =====
{
"id" : "CreateReference",
"type" : "BusinessAction",
"setupGroups" : [ "Actions" ],
"name" : "Create Reference",
"description" : null,
"scope" : "Global",
"validObjectTypes" : [ "SalesItem" ],
"allObjectTypesValid" : false,
"runPrivileged" : false,
"onApprove" : "Never",
"dependencies" : [ ]
}
*/
/*===== business rule plugin definition =====
{
"pluginId" : "JavaScriptBusinessActionWithBinds",
"binds" : [ {
"contract" : "CurrentObjectBindContract",
"alias" : "node",
"parameterClass" : "null",
"value" : null,
"description" : null
}, {
"contract" : "ReferenceTypeBindContract",
"alias" : "refType",
"parameterClass" : "com.stibo.core.domain.impl.ReferenceTypeImpl",
"value" : "PrimaryProductImage",
"description" : null
}, {
"contract" : "AssetBindContract",
"alias" : "asset",
"parameterClass" : "com.stibo.core.domain.impl.FrontAssetImpl$$Generated$$7",
"value" : "P_AC-AXPFX769",
"description" : null
} ],
"messages" : [ {
"variable" : "AssetNotFoundError",
"message" : "Asset with ID \"P_AC-AXPFX769\" could not be found",
"translations" : [ ]
} ],
"pluginType" : "Operation"
}
*/
exports.operation1 = function (node, refType, asset, AssetNotFoundError) {
if (asset == null) {
throw new AssetNotFoundError();
}
if (node.getReferences(refType).isEmpty()) {
node.createReference(asset, refType);
}
}
/*===== business rule plugin definition =====
{
"pluginId" : "ValidHierarchiesBusinessCondition",
"parameters" : [ {
"id" : "HierarchyRoots",
"type" : "java.util.List",
"values" : [ "step://product?id=I-Level1-1" ]
} ],
"pluginType" : "Precondition"
}
*/
The logic of the JavaScript operation is wrapped in a function. In the example, this function is exported in line with the Node.js module system convention. The case-sensitive property 'ConfigurationManagement.BusinessRuleConverter.ExportFormat' in the sharedconfig.properties file on the application server can be used to change this. The valid values of this property are:
-
'NodeExport' (default; Node.js module system)
-
'EcmaScriptExport' (ECMAScript module system compliant format)
-
'NoExport' (functions not exported)
The format for business libraries differs as a library in STEP already holds a number of JavaScript functions that can be called from other business rules. To make these functions available to other modules, the functions are exported when the 'NodeExport' or 'EcmaScriptExport' settings are used.
For example, assume a library has the following content:
function isProductBelow(prod, checkProdID) {
if(!isProduct(prod)) throw "Function only works with Products";
if(checkProdID == "Product hierarchy root") return true;
if(prod.getID() == "Product hierarchy root") throw "The top level Product is never below another Product.";
var currentParentId;
var currentProd = prod;
while (true) {
currentParentId = currentProd.getParent().getID();
if(currentParentId == "Product hierarchy root") return false;
else if (currentParentId == checkProdID) return true;
else currentProd = currentProd.getParent();
}
}
function isProduct(obj) {
return obj instanceof com.stibo.core.domain.Product;
}
When exported with the 'ConfigurationManagement.BusinessRuleConverter.ExportFormat' property set to the default 'NodeExport' value, the following is appended to the file, making it possible to require / import the functions from another Node.js module. Everything below, including the comment, is ignored when the library file is imported in STEP.
/*===== business library exports - this part will not be imported to STEP =====*/ exports.isProductBelow = isProductBelow exports.isProduct = isProduct
Important: While it is possible in STEP to call functions in other business libraries from within a library function, this functionality is not supported when calling the exported library functions from another module.
To allow library functions that call functions in other referenced libraries to be executable outside STEP, these can be modified so that it is possible to pass the library as a parameter. For example, assume that there is a library function like the one that follows:
//"lib" is alias for a referenced library with a function getUpc()
function setUpc(node, attributeId) {
node.getValue(attributeId).setSimpleValue(lib.getUpc());
}
This function can be modified as shown below, making it possible to pass the library as a parameter when invoking the function outside STEP.
function setUpc(node, attributeId, passedLib) {
if (lib == null) {
lib = passedLib;
}
node.getValue(attributeId).setSimpleValue(lib.getUpc());
Note: Adding an extra optional parameter does not require that the JavaScript calling the function be modified.
Options for Export
Business rules can be exported to the editable format manually or via an outbound integration endpoint (OIEP).
Manual export
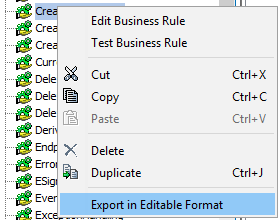
To manually export business rules individually, from a System Setup node that houses business rules, right-click and select the 'Export in Editable Format' option as shown below:
Outbound Integration Endpoint
When using the configuration management 'STEPXML Splitter' post-processor plugin for OIEPs, set the parameter 'Convert business rules to editable format' option, shown below.
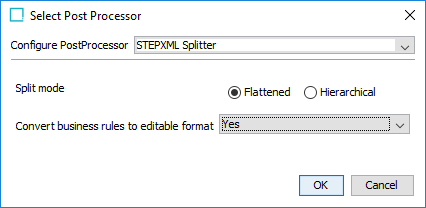
When 'Convert business rules to editable format' is set to Yes, the postprocessor converts business rules in the STEPXML to the editable format and represents them in a single *.js file instead of representing them in a STEPXML file.
For details, refer to the 'STEPXML Splitter' Post-processor Plugin in OIEP section of the Integration Endpoint Plugins for VCS Integration topic here.
Options for Import
Business rules can be imported manually or via an inbound integration endpoint (IIEP).
Manual import
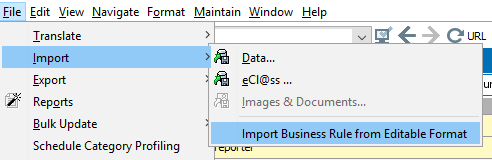
To import a single business rule manually, from the File menu, select Import and then Import Business Rule from Editable Format, as shown below.
Inbound Integration Endpoint
For importing multiple business rules via an inbound integration endpoint, the configuration management 'STEPXML Joiner' preprocessor can be used. The preprocesser accepts a .ZIP file containing STEPXML files as input as well as business rule *.js files that the preprocessor will convert to STEPXML and merge into the STEPXML file delivered to the import part of the processing.
For details, refer to the 'STEPXML Joiner' Pre-processor Plugin for IIEP section of the Integration Endpoint Plugins for VCS Integration topic here.
Note: When importing a business rule, all valid object types included in the import will be added to the existing list of valid object types for that rule.
REST Resources for Testing and Validation
Available REST resource operations allow:
-
Testing JavaScript on a running STEP server.
-
Validating the syntax of a business rule in the editable format on a STEP server.
The REST resource for testing JavaScript is available at http(s)://[step-hostname]:[step-port]/configuration-management/test-javascript?context=[context-id]&workspace=[workspace-id] and lets clients execute ECMAScript 5-compliant JavaScript on a running STEP server in a non-committing mode with access to a STEP Manager that again gives access to the standard STEP Scripting API.
As an example, POSTing the function shown below to https://[step server]/configuration-management/test-javascript?context=Context1&workspace=Main would return "Context1":
function getContextId(manager) {
return manager.getCurrentContext().getID();
}
getContextId(manager);
The resource for validating a business rule definition in the editable format is available at http(s)://[step-hostname]:[step-port]/configuration-management/validate-business-rule. The resource lets clients POST a complete business rule definition and validates the business rule in these steps:
-
Model validation - validates the overall structure and determines if the business rule metadata is correct (syntax check only).
-
Domain validation - validates existence of the operation and precondition plugin and checks if the correct parameters have been supplied (values are not checked).
-
Conversion validation - validates if the business rule definition can successfully be converted to STEPXML.
The resource returns a Boolean indicating whether or not the business rule is valid and includes a list of any encountered errors.
Example response:
{
"valid": false,
"errors": [
"'businessRuleDefinition.id': may not be null"
]
}
These REST resources:
-
Use basic authentication and the user invoking the resources must have a privilege that includes the 'Test JavaScript' setup action.
-
Require the property 'ConfigurationManagement.TestJavascript.Enabled' in the sharedconfig.properties file to be set to 'true' on systems to be used for tests and validation (defaults to 'false').
Note: There is an example step.js Node.js module that wraps the REST resources available from the STEP API Documentation page that can be used together with the documentation and examples provided.
Additional VCS information can be found in the following sections / topics: