After configuring an event processor, it must be enabled before it can run on schedule or be invoked manually. Event processors run in optimistic mode, meaning that save-points will not be created, thus decreasing execution time and increasing performance.
The status of an event processor is very important. This section addresses the different event processor status options and how to enable, invoke, or disable an event processor.
Event Processor Status Options
An event processor can be in one of several statuses: Stopped, Running, Failed (retrying), and Failed.
The table below displays each icon and a description of each event processor status.
| Icon | Enabled | Processor Status | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
No |
Stopped | The event processor has not yet been enabled or has been disabled by a user. |
|
|
Yes |
Running | The event processor is running. |
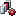
|
Yes |
Failed (retrying) | The event processor is running and retrying because of a failure. |
|
|
Yes | Failed | The event processor has stopped because of a failure. |
For more information on the 'Failed (retrying)' state, refer to the Fail and Retry Exception section below.
In the example below, a list of event processors is displayed within the Workbench on System Setup in the Event Processors node. Using the event processor status icons makes it easy to decipher the status of each of the event processors.
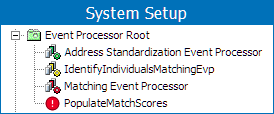
The event processor status information is also displayed in text on the Event Processor tab of the editor. For more information refer to the EP - Event Processor Tab documentation here.
When configuring and managing event processors, it is important to monitor their status, because an event processor only functions when it is enabled.
Enable Event Processor
When an event processor is created, it is in a stopped or disabled status, and must be enabled to be of use.
The steps below describe how to enable an event processor when it has been disabled or stopped because of failure.
- Go to System Setup, expand the Setup Group created for event processors, and select the Event Processor you want to enable.
- Right-click the event processor, and click Enable Event Processor.

- Confirm the event processor is now enabled by viewing the
- Enabled icon
 next to the specific event processor.
next to the specific event processor. - Enabled parameter is set to 'Yes' within the event processor editor.
- Processor Status parameter is set to 'Running', and highlighted green within the event processor editor.
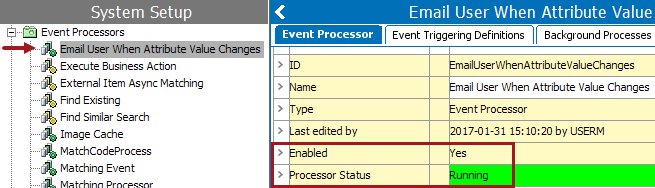
Important: If you are ready for the processor to apply the actions based on the events processed, make sure the Queue Status parameter is also set to Read Events, otherwise the enabled event processor will not function. For more information refer to the Queue Status section of the EP - Event Processor Tab topic here.
Invoke Event Processor
An event processor can only be invoked if its status is Enabled.
Steps to invoke an event processor are below.
- On the System Setup tab, select the event processor to be invoked.
- Right-click to display and select the Invoke Event Processor option.
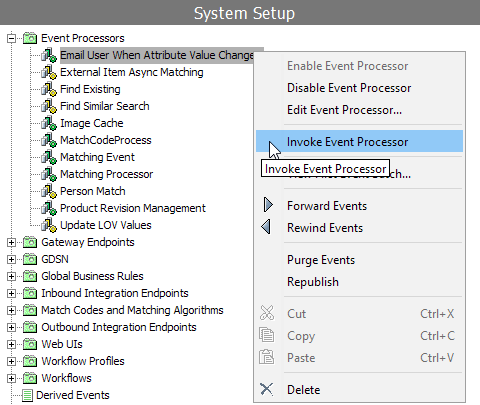
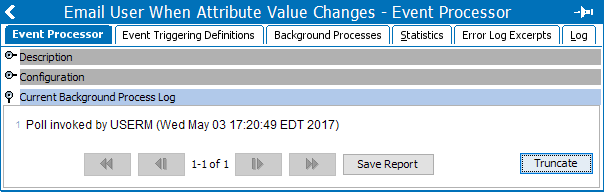
- If successful, the Current Background Process Log will display the following 'Poll invoked by (user name) (Date and Time Stamp)'.
Disable Event Processor
If an event processor is no longer necessary or needs to be stopped, a user can disable it, and if necessary, enable it later. The option to disable an event processor is only available when an event processor is in the enabled status.
The steps below describe how to disable an event processor in an enabled status.
- Go to System Setup, expand the Setup Group created for Event processors, and select the Event Processor you want to enable.
- Right-click the event processor and click Disable Event Processor.

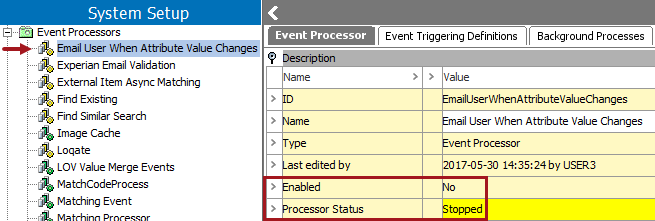
- Confirm the event processor is now disabled by viewing the:
- Disabled icon
 next to the specific event processor.
next to the specific event processor. - Enabled parameter within the event processor editor is set to 'No.'
- Processor Status parameter within the event processor editor is set to 'Stopped,' and highlighted yellow.
Generating Events from Main
By default, an approval action triggers an event for workspace revisable objects, meaning that saving an edit (but not approving it) from the Main workspace does not generate an event.
For a limited set of event processors, you can set the triggering workspace to include Main, as defined in each event processor type topic linked from the Processing Plugins topic in the System Setup documentation here.
Derived event functionality is available for triggering events prior to approval, as defined in the Derived Event topic of the System Setup documentation here.
Fail and Retry Exception
The event processor has a built-in retry logic when getting the FailAndRetryException. It enters the 'Failed (retrying)' state and retries every minute for two hours and after that every 10th minute for 30 days. When the operation eventually succeeds and the entire batch has completed, the event processor returns to its normal ‘Running’ state.
Business actions utilized in an event processor can have exception handling for certain connectivity exceptions and throw the FailAndRetryException to utilize the retry logic. This way the event processor will self-recover when the problem is solved. An example of this exception handling could be:
var request = gateway.post().path('/service/v1').urlEncodedBody(body);
try {
var response = request.invoke();
} catch (e) {
if (e.javaException instanceof com.stibo.gateway.rest.exception.RESTGatewayStatusCodeWithBodyException) {
var statusCode = e.javaException.getHttpStatusCode();
if (statusCode >= 502 && statusCode <= 504) {
throw new com.stibo.core.domain.integration.faulttolerance.FailAndRetryException("Response status " + statusCode + " (will retry failed operation after some time): " + e.javaException.toString(), e.javaException);
}
} else if (e.javaException instanceof com.stibo.gateway.rest.RESTGatewayIOException) {
throw new com.stibo.core.domain.integration.faulttolerance.FailAndRetryException("Connection issue (will retry failed operation after some time): " + e.javaException.toString(), e.javaException);
}
throw(e); // All other exceptions MUST be re-thrown
} The event processor will stop and go to the 'Failed' state when getting any other exception including the EventProcessorInterruptedException.
For more information on the FailAndRetryException and the EventProcessorInterruptedException, refer to the Java API documentation.