Attributes linked to product and classification nodes are displayed on the References tab of the product and classification of editors.
Attribute linking makes a selection of attributes available to objects that are linked to (or below) the specified node in the classification or product hierarchy.
Before linking attributes, the following issues must be considered:
Where to link an attribute
Before linking attributes, it is very important to consider the scope of these attributes, i.e., for which objects are they supposed to be relevant.
A recommended practice is to organize the Product hierarchy or the Classification hierarchy so similar products, that share the same characteristics, are grouped together. These products will then be able to share a set of attributes by inheritance from the hierarchy.
Which hierarchy levels to link to
If you have a hierarchy where an upper level node has more sub nodes that all share the same characteristics, the attributes should be linked at that upper node level. The attributes will then be inherited to the sub nodes.
If, however, the attributes only are relevant to a sub node, they should be linked there. Read about attribute inheritance below.
Which product object types to link to
It may also be important to specify which type of product the attribute is describing.
For example, attributes such as 'Price' and 'Order Code' will only be relevant to products with object type 'Article'. This means that products with object type 'Product Family' cannot have a 'Price' or an 'Order Code'.
On the other hand, an attribute such as 'Long Description' may be relevant to a 'Product Family', but not to an 'Article'.
Attribute inheritance
An attribute that is linked to a node in the hierarchy is inherited to the nodes below. This way, attributes are shared among nodes.
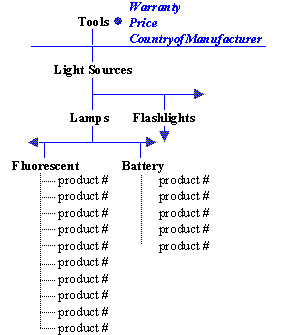
As an example, a specification attribute called 'BladeWidth' might be linked at the 'Saws' node (below the ' Power Tools' node). Therefore, the attribute 'BladeWidth' is available to both the sub nodes 'Circular Saws' and 'Table Saws', by inheritance.
This inheritance feature is useful when there are globally used attributes – these are attributes that are 'common' to all products.
Note: The inheritance feature is supported only in specification attributes.
For example, as shown in the image below, 'Warranty', 'Price', and 'CountryofManufacturer' would most likely be global attributes, since each and every product would have a value for these characteristics. Therefore, these attributes would be linked at the top node in the hierarchy, and in doing so, be inherited to all of the nodes below.