In central onboarding solutions, it is common practice to prevent duplicate records from being introduced into the MDM system. However, in situations where potential duplicates are found, there are certain scenarios to be considered, such as:
-
What is the business process when potential duplicates are found?
-
How should users cancel an onboarding process when a duplicate is selected?
For information on use cases for governing potential duplicates in central onboarding workflows, refer to the Governing Multiple Roles Within Party Data topic.
Considerations for Cancel State
When onboarding a new customer or supplier entity within MDM, the Find Similar feature is commonly used to either avoid creating duplicate records in the system, or to find existing records so further maintenance activities (such as adding new roles or lines of business) may be carried out.
In the event Find Similar returns potential duplicates, the user may choose to cancel the current onboarding activity and initiate the existing record into a maintenance workflow with proper governance. However, this leaves the system with incomplete customer or supplier records that are no longer required. The governance of such records should be managed seamlessly and in a way that does not disrupt normal day-to-day operations.
Since entities cannot be deleted from the system while they are still in a workflow, it is recommended that a ‘Cancel’ state be added to the workflow to which all canceled records can transition.
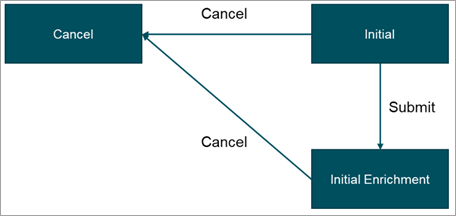
From within the 'Cancel' state, consider the following design options:
-
Allow canceled records to remain in the ‘Cancel’ state until a scheduled process creates a collection of these records, performs bulk operations to remove them from the workflow, and subsequently deletes them from the system.
-
Allow a business rule to set an attribute which flags the records for deletion and removes the records from the workflow upon entry into the ‘Cancel’ state. A scheduled background process may then create a collection of these flagged records and perform a bulk operation to delete them from the system.
This approach implies that the data model must be extended since a dedicated delete attribute is required.
Whichever approach is selected must meet the needs of the business. When users decide to cancel an onboarding activity, the deletion of these records should be out-of-mind for the users and handled in the background with no further stewardship action necessary.