There are a number of considerations before starting the setup for Kafka Receiver.
-
Capability
-
Message size limits
-
Topic partitions
-
Topic offset
-
Static membership
-
SASL authentication, if needed
Each area is explained in further detail below.
When configuring Kafka, STEPXML is recommended for the messaging format. Other formats supported for integration with STEP will also work, but the documentation has been written for STEPXML.
Compatibility
Integration with Kafka for event messaging is supported via the following versions of Apache Kafka:
-
3.5.1
-
3.4x
-
3.2x
-
3.0x
-
2.6x
-
2.5x
-
2.4x
For information on an alternate receiver option using Kafka, refer to the Kafka Streaming Receiver topic.
For information on the delivery option using Kafka, refer to the Kafka Delivery Method topic.
Message Size Limits
If messages are routinely close to the limit or there are occasional large messages, consider using compression to reduce the size of the messages.
Important: As compression can negatively impact the performance of the system, it is only recommended when there are occasional larger messages.
When you cannot avoid files larger than the 1 MB limit for an integration, consider using the REST Receiver instead of Kafka.
Topic Partitions
The Kafka Receiver can only read from single-partition topics (topics created with '--partitions 1') while the Kafka Streaming Receiver can read from multiple partitions on a topic.
Topic Offset
With Kafka Receiver, the Kafka topic offset can be managed in STEP or can be managed on Kafka for the Kafka Receiver. If some message processing fails in the importer, it is possible to roll back the transaction alongside the topic offset increment. In this scenario, transactional integrity is achieved when reading from the Kafka topic. The offset is associated with the IIEP.
Note: If you export / import IIEPs between systems, the imported endpoint always starts from offset 0. If you restore a STEP database backup, the offset will also be restored.
Static Membership
To avoid issues with Kafka rebalance, and to generally make reconnecting an endpoint to Kafka faster, a static membership is employed with the Kafka Receiver. As a result, the connection information for the IIEP on Kafka is cached for a default of up to 30 minutes. If the IIEP is scheduled to run before the 30 minutes elapse, the reconnects are a bit faster. For this reason, the session timeout in the Kafka driver is set to be 30 minutes which is the default maximum on a Kafka installation. If this is configured differently, set this timeout manually from the default setting, which is 1800000 for 30 minutes in milliseconds. To set manually, navigate to the Kafka.Receiver.<ENDPOINT-ID>.SessionTimoutInMs configuration property.
SASL Authentication
Support for Simple Authentication and Security Layer (SASL) authentication (both SASL PLAINTEXT with PLAIN and SASL_SSL with PLAIN, OAUTHBEARER, and SCRAM) is supported for the Kafka receiver and delivery options. Using SASL gives you more data security options and allows for alternatives to the other array of Kafka connector authentication functionality support, which includes support for AWS MSK, Heroku, and Aiven (with TLS Client Certificate Authentication).
Use the Self-Service UI to edit the Kafka.Receiver.Dynamic.ExtraDriverOptions configuration property, where the 'Dynamic' is the placeholder for your endpoint ID [IIEP_ID].
Important: Prior to configuration, dropdown parameters that rely on a property are empty. Hovering over the dropdown or clicking a dropdown displays the required property name to configure. To display the value(s), in the Self-Service UI, select the environment, and on the 'Configuration properties' tab, configure the property for your system. Refer to the Self-Service User Guide for information about setting configuration properties, including the use of the ${CUSTOMER_SECRETS_ROOT} and ${CUSTOMER_CONFIG_ROOT} variables.
Allow a few minutes for changes made in the Self-Service UI 'Configuration properties' tab to display in the workbench.
For SaaS systems, properties are set within the Self-Service UI by going to the Configuration Properties tab for your environment. Some changes may require you to restart the server and/or user interface (i.e., the workbench) before they take effect. If the properties you need are not shown, submit an issue within the Stibo Systems Service Portal to complete the configuration.
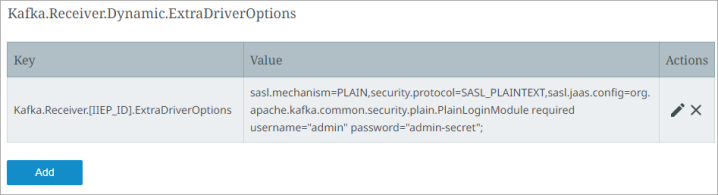
Below is an example configuration for PLAIN username/password authentication in a SaaS environment.
Configure the value of the ExtraDriverOptions as shown in the example below (you can copy this format):
-
Key field:
This should indicate the IIEP ID and must be entered as:
Kafka.Receiver.[IIEP_ID].ExtraDriverOptions (Replace [IIEP_ID] with the STEP ID of your endpoint.)
-
Value field:
Enter the following string:
sasl.mechanism=PLAIN,security.protocol=SASL_PLAINTEXT,sasl.jaas.config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.plain.PlainLoginModule required username="admin" password="admin-secret";
For SASL_SSL with PLAIN username / password authentication, the Keystore configuration in the SSL part of the Kafka receiver or delivery option can be omitted. If there is no requirement that the Kafka server has to trust the Stibo Systems SSL certificate, then none is needed. A Truststore Location / Password is required to indicate that your system trusts the Kafka Servers Certificate.
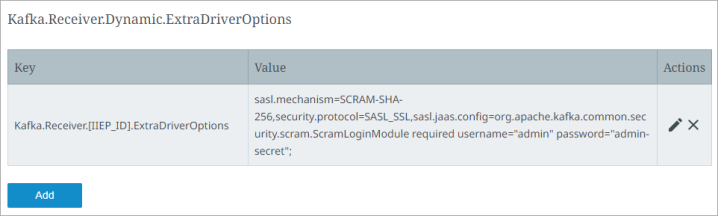
Below is a sample config for SCRAM authentication in a SaaS environment:
-
Key field:
This should indicate the IIEP ID and must be entered as:
Kafka.Receiver.[IIEP_ID].ExtraDriverOptions (Replace [IIEP_ID] with the STEP ID of your endpoint.)
-
Value Field:
Enter the following string:
sasl.mechanism=SCRAM-SHA-256,security.protocol=SASL_SSL,sasl.jaas.config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.scram.ScramLoginModule required username="admin" password="admin-secret";
All of the configuration options are taken from confluent.io documentation on how to configure SASL authentication found in this link: https://docs.confluent.io/platform/current/kafka/overview-authentication-methods.html.
Implementing various functionalities on your STEP instance requires users to add configuration properties via the Self-Service portal. For detailed instructions on how to add, remove, and manage a STEP implementation's properties, refer to the User Guide located within the Self-Service portal. To access the Self-Service portal, you can derive the Self-Service URL from the environment URL. SaaS environments always have URLs, as in this example: https://stiboqa-platform.mdm.stibosystems.com In this instance, the customer name is the first part before the dash (“stiboqa“), and the environment name is what comes after the dash and before the domain (“platform“).